Evolutionary analysis and expression profiling of the HSP70 gene family in response to abiotic stresses in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum)
- PMID: 36650980
- PMCID: PMC10358566
- DOI: 10.1177/00368504221148843
Evolutionary analysis and expression profiling of the HSP70 gene family in response to abiotic stresses in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum)
Abstract
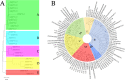
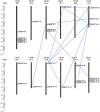
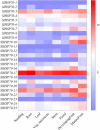
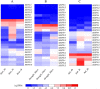
Heat shock protein 70 (HSP70) genes play essential roles in guarding plants against abiotic stresses, including heat, drought, and salt. In this study, the SlHSP70 gene family in tomatoes has been characterized using bioinformatic tools. 25 putative SlHSP70 genes in the tomato genome were found and classified into five subfamilies, with multi-subcellular localizations. Twelve pairs of gene duplications were identified, and segmental events were determined as the main factor for the gene family expansion. Based on public RNA-seq data, gene expression analysis identified the majority of genes expressed in the examined organelles. Further RNA-seq analysis and then quantitative RT-PCR validation showed that many SlHSP70 members are responsible for cellular feedback to heat, drought, and salt treatments, in which, at least five genes might be potential key players in the stress response. Our results provided a thorough overview of the SlHSP70 gene family in the tomato, which may be useful for the evolutionary and functional analysis of SlHSP70 under abiotic stress conditions.
Keywords: Abiotic stress; HSP70; evolutionary; gene expression; heat shock protein; tomato.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genome wide and evolutionary analysis of heat shock protein 70 proteins in tomato and their role in response to heat and drought stress.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Dec;49(12):11229-11241. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07734-1. Epub 2022 Jul 4. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35788950
-
Genome-Wide Analysis and Expression Profiling of SlHsp70 Gene Family in Solanum lycopersicum Revealed Higher Expression of SlHsp70-11 in Roots under Cd2+ Stress.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022 Jun 9;27(6):186. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2706186. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022. PMID: 35748262
-
The LEA gene family in tomato and its wild relatives: genome-wide identification, structural characterization, expression profiling, and role of SlLEA6 in drought stress.BMC Plant Biol. 2022 Dec 19;22(1):596. doi: 10.1186/s12870-022-03953-7. BMC Plant Biol. 2022. PMID: 36536303 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analysis and expression profiling of zinc finger homeodomain (ZHD) family genes reveal likely roles in organ development and stress responses in tomato.BMC Genomics. 2017 Sep 6;18(1):695. doi: 10.1186/s12864-017-4082-y. BMC Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28874115 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification of the WD40 Gene Family in Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.).Genes (Basel). 2023 Jun 15;14(6):1273. doi: 10.3390/genes14061273. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37372453 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptome-wide identification of the Hsp70 gene family in Pugionium cornutum and functional analysis of PcHsp70-5 under drought stress.Planta. 2024 Aug 31;260(4):84. doi: 10.1007/s00425-024-04509-9. Planta. 2024. PMID: 39214933
-
Tomato plant response to heat stress: a focus on candidate genes for yield-related traits.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Jan 8;14:1245661. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1245661. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38259925 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dixon GR. Climate change – impact on crop growth and food production, and plant pathogens. Can J Plant Pathol 2012; 34: 362–379.
-
- Ritossa F. A new puffing pattern induced by temperature shock and DNP in drosophila. Experientia 1962; 18: 571–573.
-
- Sung D-Y, Kaplan F, Guy CL. Plant Hsp70 molecular chaperones: protein structure, gene family, expression and function. Physiol Plant 2001; 113: 443–451.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

