Erythrocyte membrane with CLIPPKF as biomimetic nanodecoy traps merozoites and attaches to infected red blood cells to prevent Plasmodium infection
- PMID: 36647056
- PMCID: PMC9841648
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-022-01709-x
Erythrocyte membrane with CLIPPKF as biomimetic nanodecoy traps merozoites and attaches to infected red blood cells to prevent Plasmodium infection
Abstract
Background: Malaria remains a serious threat to global public health. With poor efficacies of vaccines and the emergence of drug resistance, novel strategies to control malaria are urgently needed.
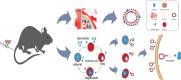
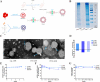
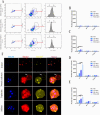
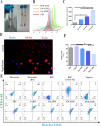
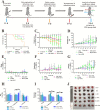
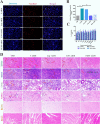
Results: We developed erythrocyte membrane-camouflaged nanoparticles loaded with artemether based on the growth characteristics of Plasmodium. The nanoparticles could capture the merozoites to inhibit them from repeatedly infecting normal erythrocytes, owing to the interactions between merozoites and heparin-like molecules on the erythrocyte membrane. Modification with a phosphatidylserine-targeting peptide (CLIPPKF) improved the drug accumulation in infected red blood cells (iRBCs) from the externalized phosphatidylserine induced by Plasmodium infection. In Plasmodium berghei ANKA strain (pbANKA)-infected C57BL/6 mice, the nanoparticles significantly attenuated Plasmodium-induced inflammation, apoptosis, and anemia. We observed reduced weight variation and prolonged survival time in pbANKA-challenged mice, and the nanoparticles showed good biocompatibility and negligible cytotoxicity.
Conclusion: Erythrocyte membrane-camouflaged nanoparticles loaded with artemether were shown to provide safe and effective protection against Plasmodium infection.
Keywords: Artemether; Erythrocyte membrane biomimetic nanomaterials; Merozoites; Targeted delivery; pbANKA-infected malaria.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Beneficial effect of aurothiomalate on murine malaria.Malar J. 2010 May 7;9:118. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-9-118. Malar J. 2010. PMID: 20459650 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of dyslipidaemia and cholesterol modulation on erythrocyte susceptibility to malaria parasite infection.Malar J. 2019 Nov 29;18(1):381. doi: 10.1186/s12936-019-3016-3. Malar J. 2019. PMID: 31783858 Free PMC article.
-
A Thioredoxin Homologous Protein of Plasmodium falciparum Participates in Erythrocyte Invasion.Infect Immun. 2018 Jul 23;86(8):e00289-18. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00289-18. Print 2018 Aug. Infect Immun. 2018. PMID: 29844242 Free PMC article.
-
The Cellular and Molecular Interaction Between Erythrocytes and Plasmodium falciparum Merozoites.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Mar 31;12:816574. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.816574. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35433504 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Erythrocyte invasion receptors for Plasmodium falciparum: new and old.Transfus Med. 2016 Apr;26(2):77-88. doi: 10.1111/tme.12280. Epub 2016 Feb 9. Transfus Med. 2016. PMID: 26862042 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- SDD2018-04/Open Research Fund of Key Laboratory of Smart Drug Delivery
- SDD2022-01/Open Research Fund of Key Laboratory of Smart Drug Delivery
- 2020A1515110336/Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation
- A1-2601-21-414-001Z22/Xinglin young scholar construction of high levels university projects of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine
- 81873218/Natural Science Foundation of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

