Targeted therapy for head and neck cancer: signaling pathways and clinical studies
- PMID: 36646686
- PMCID: PMC9842704
- DOI: 10.1038/s41392-022-01297-0
Targeted therapy for head and neck cancer: signaling pathways and clinical studies
Abstract
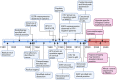
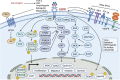
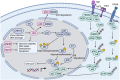
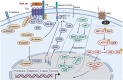
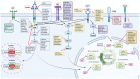
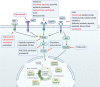
Head and neck cancer (HNC) is malignant, genetically complex and difficult to treat and is the sixth most frequent cancer, with tobacco, alcohol and human papillomavirus being major risk factors. Based on epigenetic data, HNC is remarkably heterogeneous, and treatment remains challenging. There is a lack of significant improvement in survival and quality of life in patients with HNC. Over half of HNC patients experience locoregional recurrence or distal metastasis despite the current multiple traditional therapeutic strategies and immunotherapy. In addition, resistance to chemotherapy, radiotherapy and some targeted therapies is common. Therefore, it is urgent to explore more effective and tolerable targeted therapies to improve the clinical outcomes of HNC patients. Recent targeted therapy studies have focused on identifying promising biomarkers and developing more effective targeted therapies. A well understanding of the pathogenesis of HNC contributes to learning more about its inner association, which provides novel insight into the development of small molecule inhibitors. In this review, we summarized the vital signaling pathways and discussed the current potential therapeutic targets against critical molecules in HNC, as well as presenting preclinical animal models and ongoing or completed clinical studies about targeted therapy, which may contribute to a more favorable prognosis of HNC. Targeted therapy in combination with other therapies and its limitations were also discussed.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Head and neck cancer: pathogenesis and targeted therapy.MedComm (2020). 2024 Aug 21;5(9):e702. doi: 10.1002/mco2.702. eCollection 2024 Sep. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 39170944 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic signature associated with radioresistance in head and neck cancer via transcriptomic and bioinformatic analyses.BMC Cancer. 2019 Jan 14;19(1):64. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-5243-3. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30642292 Free PMC article.
-
RTKs in pathobiology of head and neck cancers.Adv Cancer Res. 2020;147:319-373. doi: 10.1016/bs.acr.2020.04.008. Epub 2020 Jun 15. Adv Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32593405 Review.
-
Photodynamic therapy with 5-aminolevulinic acid (ALA) impairs tumor initiating and chemo-resistance property in head and neck cancer-derived cancer stem cells.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 24;9(1):e87129. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087129. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24475244 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer stem cells in head and neck cancer: A Mini Review.Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2015 Oct 30;61(6):39-43. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2015. PMID: 26518895 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular pathways and therapeutic strategies in dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP): unravelling the tumor's genetic landscape.EXCLI J. 2024 May 14;23:727-762. doi: 10.17179/excli2024-7164. eCollection 2024. EXCLI J. 2024. PMID: 38983783 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bufalin Suppresses Head and Neck Cancer Development by Modulating Immune Responses and Targeting the β-Catenin Signaling Pathway.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Aug 1;16(15):2739. doi: 10.3390/cancers16152739. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39123466 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological impact of microRNAs in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Prevailing insights on molecular pathways, diagnosis, and nanomedicine treatment.Front Pharmacol. 2023 May 3;14:1174330. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1174330. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37205904 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Critical review of the current and future prospects of VEGF-TKIs in the management of squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck.Front Oncol. 2023 Dec 13;13:1310106. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1310106. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 38192624 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel pipeline for prioritizing cancer type-specific therapeutic vulnerabilities using DepMap identifies PAK2 as a target in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas.Mol Oncol. 2024 Feb;18(2):336-349. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.13558. Epub 2023 Dec 13. Mol Oncol. 2024. PMID: 37997254 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

