xAtlas: scalable small variant calling across heterogeneous next-generation sequencing experiments
- PMID: 36644891
- PMCID: PMC9841152
- DOI: 10.1093/gigascience/giac125
xAtlas: scalable small variant calling across heterogeneous next-generation sequencing experiments
Abstract
Background: The growing volume and heterogeneity of next-generation sequencing (NGS) data complicate the further optimization of identifying DNA variation, especially considering that curated high-confidence variant call sets frequently used to validate these methods are generally developed from the analysis of comparatively small and homogeneous sample sets.
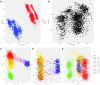
Findings: We have developed xAtlas, a single-sample variant caller for single-nucleotide variants (SNVs) and small insertions and deletions (indels) in NGS data. xAtlas features rapid runtimes, support for CRAM and gVCF file formats, and retraining capabilities. xAtlas reports SNVs with 99.11% recall and 98.43% precision across a reference HG002 sample at 60× whole-genome coverage in less than 2 CPU hours. Applying xAtlas to 3,202 samples at 30× whole-genome coverage from the 1000 Genomes Project achieves an average runtime of 1.7 hours per sample and a clear separation of the individual populations in principal component analysis across called SNVs.
Conclusions: xAtlas is a fast, lightweight, and accurate SNV and small indel calling method. Source code for xAtlas is available under a BSD 3-clause license at https://github.com/jfarek/xatlas.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press GigaScience.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
SNVSniffer: an integrated caller for germline and somatic single-nucleotide and indel mutations.BMC Syst Biol. 2016 Aug 1;10 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):47. doi: 10.1186/s12918-016-0300-5. BMC Syst Biol. 2016. PMID: 27489955 Free PMC article.
-
Tool evaluation for the detection of variably sized indels from next generation whole genome and targeted sequencing data.PLoS Comput Biol. 2022 Feb 17;18(2):e1009269. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1009269. eCollection 2022 Feb. PLoS Comput Biol. 2022. PMID: 35176018 Free PMC article.
-
A study on fast calling variants from next-generation sequencing data using decision tree.BMC Bioinformatics. 2018 Apr 19;19(1):145. doi: 10.1186/s12859-018-2147-9. BMC Bioinformatics. 2018. PMID: 29673316 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of variant identification methods for whole genome sequencing data in dairy cattle.BMC Genomics. 2014 Nov 1;15(1):948. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-948. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 25361890 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the Calling Performance of a Rare Disease NGS Panel for Single Nucleotide and Copy Number Variants.Mol Diagn Ther. 2017 Jun;21(3):303-313. doi: 10.1007/s40291-017-0268-x. Mol Diagn Ther. 2017. PMID: 28290094
Cited by
-
Identification of Rare Variants Involved in High Myopia Unraveled by Whole Genome Sequencing.Ophthalmol Sci. 2023 Apr 6;3(4):100303. doi: 10.1016/j.xops.2023.100303. eCollection 2023 Dec. Ophthalmol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37250922 Free PMC article.
-
Deep clinicopathological phenotyping identifies a previously unrecognized pathogenic EMD splice variant.Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2021 Oct;8(10):2052-2058. doi: 10.1002/acn3.51454. Epub 2021 Sep 15. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2021. PMID: 34524739 Free PMC article.
-
VCPA: genomic variant calling pipeline and data management tool for Alzheimer's Disease Sequencing Project.Bioinformatics. 2019 May 15;35(10):1768-1770. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty894. Bioinformatics. 2019. PMID: 30351394 Free PMC article.
-
Absence of increased genomic variants in the cyanobacterium Chroococcidiopsis exposed to Mars-like conditions outside the space station.Sci Rep. 2022 May 19;12(1):8437. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-12631-5. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35589950 Free PMC article.
-
High prevalence of multilocus pathogenic variation in neurodevelopmental disorders in the Turkish population.Am J Hum Genet. 2021 Oct 7;108(10):1981-2005. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2021.08.009. Epub 2021 Sep 28. Am J Hum Genet. 2021. PMID: 34582790 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

