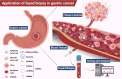
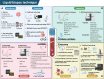
Clinical application and detection techniques of liquid biopsy in gastric cancer
- PMID: 36627698
- PMCID: PMC9832643
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-023-01715-z
Clinical application and detection techniques of liquid biopsy in gastric cancer
Abstract
Gastric cancer (GC) is one of the most common tumors worldwide and the leading cause of tumor-related mortality. Endoscopy and serological tumor marker testing are currently the main methods of GC screening, and treatment relies on surgical resection or chemotherapy. However, traditional examination and treatment methods are more harmful to patients and less sensitive and accurate. A minimally invasive method to respond to GC early screening, prognosis monitoring, treatment efficacy, and drug resistance situations is urgently needed. As a result, liquid biopsy techniques have received much attention in the clinical application of GC. The non-invasive liquid biopsy technique requires fewer samples, is reproducible, and can guide individualized patient treatment by monitoring patients' molecular-level changes in real-time. In this review, we introduced the clinical applications of circulating tumor cells, circulating free DNA, circulating tumor DNA, non-coding RNAs, exosomes, and proteins, which are the primary markers in liquid biopsy technology in GC. We also discuss the current limitations and future trends of liquid biopsy technology as applied to early clinical biopsy technology.
Keywords: Circulating tumor DNA; Circulating tumor cells; Exosomes; Gastric cancer; Liquid biopsy; Non-coding RNAs.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Liquid biopsy in gastric cancer: predictive and prognostic biomarkers.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Oct 27;13(10):903. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05350-2. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 36302755 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Liquid biopsy in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: circulating tumor cells, circulating tumor DNA, and exosomes.Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2020 Dec;20(12):1213-1227. doi: 10.1080/14737159.2020.1855977. Epub 2020 Dec 30. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2020. PMID: 33232189 Review.
-
Liquid biopsy at the frontier of detection, prognosis and progression monitoring in colorectal cancer.Mol Cancer. 2022 Mar 25;21(1):86. doi: 10.1186/s12943-022-01556-2. Mol Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35337361 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Liquid biopsy: Circulating exosomal long noncoding RNAs in cancer.Clin Chim Acta. 2019 Aug;495:331-337. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2019.04.082. Epub 2019 May 2. Clin Chim Acta. 2019. PMID: 31054913 Review.
-
Liquid biopsy of gastric cancer patients: circulating tumor cells and cell-free nucleic acids.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Mar 28;20(12):3265-86. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i12.3265. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 24696609 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Novel Biomarkers of Gastric Cancer: Current Research and Future Perspectives.J Clin Med. 2023 Jul 12;12(14):4646. doi: 10.3390/jcm12144646. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37510761 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrated analysis of single-cell and bulk RNA-seq establishes a novel signature for prediction in gastric cancer.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2023 Jul 15;15(7):1215-1226. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v15.i7.1215. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37546563 Free PMC article.
-
Current research status of tumor cell biomarker detection.Microsyst Nanoeng. 2023 Oct 5;9:123. doi: 10.1038/s41378-023-00581-5. eCollection 2023. Microsyst Nanoeng. 2023. PMID: 37811123 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Upregulation of circRNA_0023685 promotes gastric cancer progression via a circRNA-miRNA-mRNA interaction network.Am J Cancer Res. 2024 Jan 15;14(1):130-144. doi: 10.62347/TGBA1922. eCollection 2024. Am J Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38323291 Free PMC article.
-
Detection and Characterization of Methylated Circulating Tumor DNA in Gastric Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 5;25(13):7377. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137377. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000483 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

