Peripheral CD4 +CD8 + double positive T cells: A potential marker to evaluate renal impairment susceptibility during systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 36625011
- PMCID: PMC9898043
- DOI: 10.7555/JBR.36.20220094
Peripheral CD4 +CD8 + double positive T cells: A potential marker to evaluate renal impairment susceptibility during systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
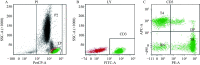
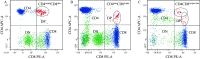
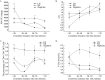
Lupus nephritis (LN) has a high incidence in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients, but there is a lack of sensitive predictive markers. The purpose of the study was to investigate the association between the CD4 +CD8 + double positive T (DPT) lymphocytes and LN. The study included patients with SLE without renal impairment (SLE-NRI), LN, nephritic syndrome (NS), or nephritis. Peripheral blood lymphocyte subsets were analyzed by flow cytometry. Biochemical measurements were performed with peripheral blood in accordance with the recommendations proposed by the National Center for Clinical Laboratories. The proportions of DPT cells in the LN group were significantly higher than that in the SLE-NRI group ( t=4.012, P<0.001), NS group ( t=3.240, P=0.001), and nephritis group ( t=2.57, P=0.011). In the LN group, the risk of renal impairment increased significantly in a DPT cells proportion-dependent manner. The risk of LN was 5.136 times (95% confidence interval, 2.115-12.473) higher in cases with a high proportion of DPT cells than those whose proportion of DPT cells within the normal range. These findings indicated that the proportion of DPT cells could be a potential marker to evaluate LN susceptibility, and the interference of NS and nephritis could be effectively excluded when assessing the risk of renal impairment during SLE with DPT cell proportion.
Keywords: CD4+CD8+ double positive T cells; lupus nephritis; susceptibility; systemic lupus erythematosus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors reported no conflict of interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
SAP-expressing T peripheral helper cells identify systemic lupus erythematosus patients with lupus nephritis.Front Immunol. 2024 Mar 14;15:1327437. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1327437. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38550577 Free PMC article.
-
Peripheral blood T-cell subset and its clinical significance in lupus nephritis patients.Lupus Sci Med. 2022 Aug;9(1):e000717. doi: 10.1136/lupus-2022-000717. Lupus Sci Med. 2022. PMID: 35973743 Free PMC article.
-
Double positive CD4+CD8+ T cells: key suppressive role in the production of autoantibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus.Indian J Med Res. 2014 Oct;140(4):513-9. Indian J Med Res. 2014. PMID: 25488445 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic lupus erythematosus, lupus nephritis and end-stage renal disease: a pragmatic review mapping disease severity and progression.Lupus. 2020 Aug;29(9):1011-1020. doi: 10.1177/0961203320932219. Epub 2020 Jun 22. Lupus. 2020. PMID: 32571142 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Complement C4d as a biomarker for systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis.Lupus. 2024 Feb;33(2):111-120. doi: 10.1177/09612033231226351. Epub 2024 Jan 16. Lupus. 2024. PMID: 38227433 Review.
Cited by
-
Characteristics and clustering analysis of peripheral blood lymphocyte subsets in children with systemic lupus erythematosus complicated with clinical infection.Clin Rheumatol. 2023 Dec;42(12):3299-3309. doi: 10.1007/s10067-023-06716-3. Epub 2023 Aug 4. Clin Rheumatol. 2023. PMID: 37537315
-
Regulatory effect of Pseudomonas aeruginosa mannose-sensitive hemagglutinin on inflammation and immune function in percutaneous nephrolithotomy patients with upper urinary tract calculi complicated with infection.Front Immunol. 2023 Jun 12;14:1181688. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1181688. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37377966 Free PMC article.
-
Legend or Truth: Mature CD4+CD8+ Double-Positive T Cells in the Periphery in Health and Disease.Biomedicines. 2023 Oct 5;11(10):2702. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11102702. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37893076 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

