Computational characterization of recombinase circuits for periodic behaviors
- PMID: 36619981
- PMCID: PMC9812718
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.105624
Computational characterization of recombinase circuits for periodic behaviors
Abstract
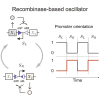
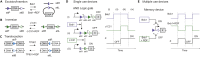
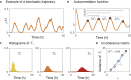
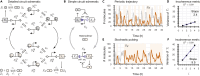
Recombinases are site-specific proteins found in nature that are capable of rearranging DNA. This function has made them promising gene editing tools in synthetic biology, as well as key elements in complex artificial gene circuits implementing Boolean logic. However, since DNA rearrangement is irreversible, it is still unclear how to use recombinases to build dynamic circuits like oscillators. In addition, this goal is challenging because a few molecules of recombinase are enough for promoter inversion, generating inherent stochasticity at low copy number. Here, we propose six different circuit designs for recombinase-based oscillators operating at a single copy number. We model them in a stochastic setting, leveraging the Gillespie algorithm for extensive simulations, and show that they can yield coherent periodic behaviors. Our results support the experimental realization of recombinase-based oscillators and, more generally, the use of recombinases to generate dynamic behaviors in synthetic biology.
Keywords: Biocomputational method; Bioengineering; Synthetic biology.
© 2022 The Authors.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Logic Synthesis of Recombinase-Based Genetic Circuits.Sci Rep. 2017 Oct 9;7(1):12873. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-07386-3. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28993615 Free PMC article.
-
Computational Methods for the Design of Recombinase Logic Circuits with Adaptable Circuit Specifications.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2553:155-171. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2617-7_8. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36227543
-
Computational Methods for the Design of Recombinase Logic Circuits.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2189:31-43. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-0822-7_3. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33180291
-
Synthetic genetic circuits for programmable biological functionalities.Biotechnol Adv. 2019 Nov 1;37(6):107393. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2019.04.015. Epub 2019 Apr 30. Biotechnol Adv. 2019. PMID: 31051208 Review.
-
Synthetic biology: insights into biological computation.Integr Biol (Camb). 2016 Apr 18;8(4):518-32. doi: 10.1039/c5ib00274e. Epub 2016 Apr 13. Integr Biol (Camb). 2016. PMID: 27074335 Review.
References
-
- Romond P.C., Guilmot J.M., Goldbeter A. The mitotic oscillator: temporal self-organization in a phosphorylation-dephosphorylation enzymatic cascade. Berichte der Bunsengesellschaft für. physikalische Chemie. 1994;98:1152–1159.
-
- Barkai N., Leibler S. Circadian clocks limited by noise. Nature. 2000;403:267–268. - PubMed
-
- Uriu K., Morishita Y., Iwasa Y. Synchronized oscillation of the segmentation clock gene in vertebrate development. J. Math. Biol. 2010;61:207–229. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

