A transcriptome analysis of Benincasa hispida revealed the pathways and genes involved in response to Phytophthora melonis infection
- PMID: 36618646
- PMCID: PMC9815465
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1106123
A transcriptome analysis of Benincasa hispida revealed the pathways and genes involved in response to Phytophthora melonis infection
Abstract
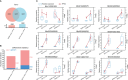
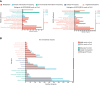
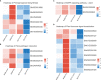
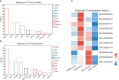
Wilt disease caused by Phytophthora melonis infection is one of the most serious threats to Benincasa hispida production. However, the mechanism of the response of B. hispida to a P. melonis infection remains largely unknown. In the present study, two B. hispida cultivars with different degrees of resistance to P. melonis were identified: B488 (a moderately resistant cultivar) and B214 (a moderately susceptible cultivar). RNA-seq was performed on P. melonis-infected B488 and B214 12 hours post infection (hpi). Compared with the control, 680 and 988 DEGs were respectively detected in B488 and B214. A KEGG pathway analysis combined with a cluster analysis revealed that phenylpropanoid biosynthesis, plant-pathogen interaction, the MAPK signaling pathway-plant, and plant hormone signal transduction were the most relevant pathways during the response of both B488 and B214 to P. melonis infection, as well as the differentially expressed genes in the two cultivars. In addition, a cluster analysis of transcription factor genes in DEGs identified four genes upregulated in B488 but not in B214 at 6 hpi and 12 hpi, which was confirmed by qRT-PCR. These were candidate genes for elucidating the mechanism of the B. hispida response to P. melonis infection and laying the foundation for the improvement of B. hispida.
Keywords: Benincasa hispida; Phytophthora melonis; RNA-Seq; resistanceassociated gene; wilt disease.
Copyright © 2022 Cai, Yang, Liu, Yan, Jiang and Xie.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Expression analysis of defense-related genes in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) against Phytophthora melonis.Mol Biol Rep. 2020 Jul;47(7):4933-4944. doi: 10.1007/s11033-020-05520-5. Epub 2020 Jun 12. Mol Biol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32533402
-
Transcriptome-based analysis of candidate gene markers associated with resistance mechanism to Phytophthora melonis that causes root and crown rot in pumpkin.Funct Plant Biol. 2024 Jan;51:FP23038. doi: 10.1071/FP23038. Funct Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 38207292
-
Transcriptome Analysis of the Melon-Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. melonis Race 1.2 Pathosystem in Susceptible and Resistant Plants.Front Plant Sci. 2017 Mar 17;8:362. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.00362. eCollection 2017. Front Plant Sci. 2017. PMID: 28367157 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression analysis of resistant and susceptible rice cultivars to sheath blight after inoculation with Rhizoctonia solani.BMC Genomics. 2022 Apr 7;23(1):278. doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-08524-6. BMC Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35392815 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative transcriptome provides insights into gene regulation network associated with the resistance to Fusarium wilt in grafted wax gourd Benincasa hispida.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Oct 27;14:1277500. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1277500. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37964995 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

