Cdc42 regulates cytokine expression and trafficking in bronchial epithelial cells
- PMID: 36618374
- PMCID: PMC9816864
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1069499
Cdc42 regulates cytokine expression and trafficking in bronchial epithelial cells
Abstract
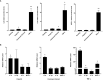
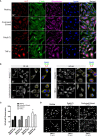
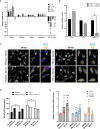
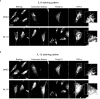
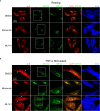
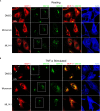
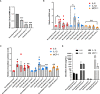
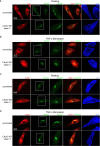
Airway epithelial cells can respond to incoming pathogens, allergens and stimulants through the secretion of cytokines and chemokines. These pro-inflammatory mediators activate inflammatory signaling cascades that allow a robust immune response to be mounted. However, uncontrolled production and release of cytokines and chemokines can result in chronic inflammation and appears to be an underlying mechanism for the pathogenesis of pulmonary disorders such as asthma and COPD. The Rho GTPase, Cdc42, is an important signaling molecule that we hypothesize can regulate cytokine production and release from epithelial cells. We treated BEAS-2B lung epithelial cells with a set of stimulants to activate inflammatory pathways and cytokine release. The production, trafficking and secretion of cytokines were assessed when Cdc42 was pharmacologically inhibited with ML141 drug or silenced with lentiviral-mediated shRNA knockdown. We found that Cdc42 inhibition with ML141 differentially affected gene expression of a subset of cytokines; transcription of IL-6 and IL-8 were increased while MCP-1 was decreased. However, Cdc42 inhibition or depletion disrupted IL-8 trafficking and reduced its secretion even though transcription was increased. Cytokines transiting through the Golgi were particularly affected by Cdc42 disruption. Our results define a role for Cdc42 in the regulation of cytokine production and release in airway epithelial cells. This underscores the role of Cdc42 in coupling receptor activation to downstream gene expression and also as a regulator of cytokine secretory pathways.
Keywords: Rho GTPase; cytokine; epithelial cells; golgi; lung inflammation; secretion.
Copyright © 2022 Shouib and Eitzen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inflammatory gene regulation by Cdc42 in airway epithelial cells.Cell Signal. 2024 Oct;122:111321. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2024.111321. Epub 2024 Jul 25. Cell Signal. 2024. PMID: 39067837
-
Chemokine production by the BEAS-2B human bronchial epithelial cells: differential regulation of eotaxin, IL-8, and RANTES by TH2- and TH1-derived cytokines.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2000 Jan;105(1 Pt 1):126-33. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(00)90187-8. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10629462
-
Interleukin-31 induces cytokine and chemokine production from human bronchial epithelial cells through activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase signalling pathways: implications for the allergic response.Immunology. 2007 Dec;122(4):532-41. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2007.02668.x. Epub 2007 Jul 11. Immunology. 2007. PMID: 17627770 Free PMC article.
-
Bronchial epithelial cell-cytokine interactions in airway inflammation.J Investig Med. 1995 Jun;43(3):241-9. J Investig Med. 1995. PMID: 7614070 Review.
-
Diesel exhaust particles activate human bronchial epithelial cells to express inflammatory mediators in the airways: a review.Respirology. 2000 Jun;5(2):197-203. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1843.2000.00245.x. Respirology. 2000. PMID: 10894110 Review.
Cited by
-
Cell Division Cycle 42 Improves Renal Functions, Fibrosis, Th1/Th17 Infiltration and Inflammation to Some Degree in Diabetic Nephropathy.Inflammation. 2024 Nov 13. doi: 10.1007/s10753-024-02169-1. Online ahead of print. Inflammation. 2024. PMID: 39535664
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

