Multiple Roles of PLK1 in Mitosis and Meiosis
- PMID: 36611980
- PMCID: PMC9818836
- DOI: 10.3390/cells12010187
Multiple Roles of PLK1 in Mitosis and Meiosis
Abstract
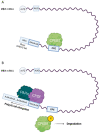
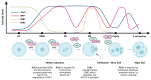
Cells are equipped with a diverse network of signaling and regulatory proteins that function as cell cycle regulators and checkpoint proteins to ensure the proper progression of cell division. A key regulator of cell division is polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1), a member of the serine/threonine kinase family that plays an important role in regulating the mitotic and meiotic cell cycle. The phosphorylation of specific substrates mediated by PLK1 controls nuclear envelope breakdown (NEBD), centrosome maturation, proper spindle assembly, chromosome segregation, and cytokinesis. In mammalian oogenesis, PLK1 is essential for resuming meiosis before ovulation and for establishing the meiotic spindle. Among other potential roles, PLK1 regulates the localized translation of spindle-enriched mRNAs by phosphorylating and thereby inhibiting the translational repressor 4E-BP1, a downstream target of the mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin) pathway. In this review, we summarize the functions of PLK1 in mitosis, meiosis, and cytokinesis and focus on the role of PLK1 in regulating mRNA translation. However, knowledge of the role of PLK1 in the regulation of meiosis remains limited.
Keywords: PLK1; mRNA translation; meiosis; mitosis; oocytes; polo-like kinase 1; spindle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
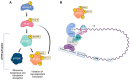
Similar articles
-
Multiple requirements of PLK1 during mouse oocyte maturation.PLoS One. 2015 Feb 6;10(2):e0116783. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0116783. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25658810 Free PMC article.
-
Polo-like kinase 1 regulates activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) at the mitotic apparatus.Cell Cycle. 2011 Apr 15;10(8):1295-302. doi: 10.4161/cc.10.8.15342. Epub 2011 Apr 15. Cell Cycle. 2011. PMID: 21474997
-
Polo-like kinase 1 is essential for the first mitotic division in the mouse embryo.Mol Reprod Dev. 2013 Jul;80(7):522-34. doi: 10.1002/mrd.22188. Epub 2013 Jun 13. Mol Reprod Dev. 2013. PMID: 23649868
-
Playing polo during mitosis: PLK1 takes the lead.Oncogene. 2017 Aug 24;36(34):4819-4827. doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.113. Epub 2017 Apr 24. Oncogene. 2017. PMID: 28436952 Review.
-
Regulating a key mitotic regulator, polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1).Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2018 Nov;75(11):481-494. doi: 10.1002/cm.21504. Epub 2018 Dec 7. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2018. PMID: 30414309 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Anoikis resistance regulates immune infiltration and drug sensitivity in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma: insights from multi omics, single cell analysis and in vitro experiment.Front Immunol. 2024 Jun 17;15:1427475. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1427475. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38953023 Free PMC article.
-
NOD2 reduces the chemoresistance of melanoma by inhibiting the TYMS/PLK1 signaling axis.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Oct 1;15(10):720. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-07104-8. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 39353904 Free PMC article.
-
AKT Inhibition Sensitizes to Polo-Like Kinase 1 Inhibitor Onvansertib in Prostate Cancer.Mol Cancer Ther. 2024 Oct 1;23(10):1404-1417. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-23-0933. Mol Cancer Ther. 2024. PMID: 38894678
-
CYR61 Acts as an Intracellular Microtubule-Associated Protein and Coordinates Mitotic Progression via PLK1-FBW7 Pathway.Int J Biol Sci. 2024 Jun 3;20(8):3140-3155. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.93335. eCollection 2024. Int J Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38904029 Free PMC article.
-
The multifaceted functions of DNA-PKcs: implications for the therapy of human diseases.MedComm (2020). 2024 Jun 19;5(7):e613. doi: 10.1002/mco2.613. eCollection 2024 Jul. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 38898995 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

