12- O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate Reduces Activation of Hepatic Stellate Cells by Inhibiting the Hippo Pathway Transcriptional Coactivator YAP
- PMID: 36611885
- PMCID: PMC9818550
- DOI: 10.3390/cells12010091
12- O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate Reduces Activation of Hepatic Stellate Cells by Inhibiting the Hippo Pathway Transcriptional Coactivator YAP
Abstract
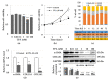
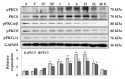
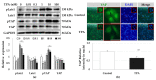
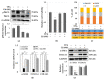
Although protein kinase C (PKC) regulates various biological activities, including cell proliferation, differentiation, migration, tissue remodeling, gene expression, and cell death, the antifibrotic effect of PKC in myofibroblasts is not fully understood. We investigated whether 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA), a PKC activator, reduced the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) and explored the involvement of the Hippo pathway transcriptional coactivator YAP. We analyzed the effect of TPA on the proliferation and expression of α-smooth muscle actin (SMA) in the LX-2 HSC line. We also analyzed the phosphorylation of the Hippo pathway molecules YAP and LATS1 and investigated YAP nuclear translocation. We examined whether Gö 6983, a pan-PKC inhibitor, restored the TPA-inhibited activities of HSCs. Administration of TPA decreased the growth rate of LX-2 cells and inhibited the expression of α-SMA and collagen type I alpha 1 (COL1A1). In addition, TPA induced phosphorylation of PKCδ, LATS1, and YAP and inhibited the nuclear translocation of YAP compared with the control. These TPA-induced phenomena were mostly ameliorated by Gö 6983. Our results indicate that PKCδ exerts an antifibrotic effect by inhibiting the Hippo pathway in HSCs. Therefore, PKCδ and YAP can be used as therapeutic targets for the treatment of fibrotic diseases.
Keywords: 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate; Yes-associated protein 1; hepatic stellate cell; protein kinase Cδ.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Liquiritigenin inhibits hepatic fibrogenesis and TGF-β1/Smad with Hippo/YAP signal.Phytomedicine. 2019 Sep;62:152780. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.12.003. Epub 2018 Dec 10. Phytomedicine. 2019. PMID: 31121384
-
Proliferation of hepatic stellate cells, mediated by YAP and TAZ, contributes to liver repair and regeneration after liver ischemia-reperfusion injury.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2018 Apr 1;314(4):G471-G482. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00153.2017. Epub 2018 Jan 11. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29351389 Free PMC article.
-
Physalin D attenuates hepatic stellate cell activation and liver fibrosis by blocking TGF-β/Smad and YAP signaling.Phytomedicine. 2020 Nov;78:153294. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153294. Epub 2020 Jul 28. Phytomedicine. 2020. PMID: 32771890
-
YAP and the Hippo pathway in cholangiocarcinoma.J Gastroenterol. 2019 Jun;54(6):485-491. doi: 10.1007/s00535-019-01563-z. Epub 2019 Feb 27. J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 30815737 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reciprocal regulation of YAP/TAZ by the Hippo pathway and the Small GTPase pathway.Small GTPases. 2020 Jul;11(4):280-288. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2018.1435986. Epub 2018 Apr 20. Small GTPases. 2020. PMID: 29457552 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Fisetin in Cancer: Attributes, Developmental Aspects, and Nanotherapeutics.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Jan 28;16(2):196. doi: 10.3390/ph16020196. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37259344 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring lncRNA Expression Patterns in Patients With Hypertrophied Ligamentum Flavum.Neurospine. 2024 Mar;21(1):330-341. doi: 10.14245/ns.2346994.497. Epub 2024 Jan 29. Neurospine. 2024. PMID: 38291747 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

