Dynamic regulation of RAS and RAS signaling
- PMID: 36607281
- PMCID: PMC9988006
- DOI: 10.1042/BCJ20220234
Dynamic regulation of RAS and RAS signaling
Abstract
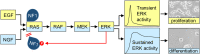
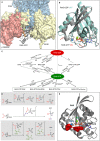
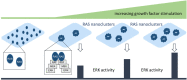
RAS proteins regulate most aspects of cellular physiology. They are mutated in 30% of human cancers and 4% of developmental disorders termed Rasopathies. They cycle between active GTP-bound and inactive GDP-bound states. When active, they can interact with a wide range of effectors that control fundamental biochemical and biological processes. Emerging evidence suggests that RAS proteins are not simple on/off switches but sophisticated information processing devices that compute cell fate decisions by integrating external and internal cues. A critical component of this compute function is the dynamic regulation of RAS activation and downstream signaling that allows RAS to produce a rich and nuanced spectrum of biological outputs. We discuss recent findings how the dynamics of RAS and its downstream signaling is regulated. Starting from the structural and biochemical properties of wild-type and mutant RAS proteins and their activation cycle, we examine higher molecular assemblies, effector interactions and downstream signaling outputs, all under the aspect of dynamic regulation. We also consider how computational and mathematical modeling approaches contribute to analyze and understand the pleiotropic functions of RAS in health and disease.
Keywords: RAS proteins; biological networks; cancer; dynamics; signaling.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
W.K. is consulting for Boehringer Ingelheim. The other authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Functional and structural insights into RAS effector proteins.Mol Cell. 2024 Aug 8;84(15):2807-2821. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2024.06.027. Epub 2024 Jul 17. Mol Cell. 2024. PMID: 39025071 Review.
-
Relation between the conformational heterogeneity and reaction cycle of Ras: molecular simulation of Ras.Biophys J. 2010 Dec 1;99(11):3726-34. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2010.09.063. Biophys J. 2010. PMID: 21112297 Free PMC article.
-
Differential dynamics of RAS isoforms in GDP- and GTP-bound states.Proteins. 2015 Jun;83(6):1091-106. doi: 10.1002/prot.24805. Epub 2015 Apr 22. Proteins. 2015. PMID: 25846136
-
[Structures and functions of small GTPase and heterotrimeric G proteins].Nihon Rinsho. 1998 Jul;56(7):1750-5. Nihon Rinsho. 1998. PMID: 9702049 Review. Japanese.
-
Ras Conformational Ensembles, Allostery, and Signaling.Chem Rev. 2016 Jun 8;116(11):6607-65. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00542. Epub 2016 Jan 27. Chem Rev. 2016. PMID: 26815308 Review.
Cited by
-
Mathematical Modeling and Inference of Epidermal Growth Factor-Induced Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Cell Signaling Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 23;25(18):10204. doi: 10.3390/ijms251810204. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337687 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PIP5K-Ras bistability initiates plasma membrane symmetry breaking to regulate cell polarity and migration.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 15:2024.09.15.613115. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.15.613115. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39314378 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
MRTX1133's promise for treating KRASG12D-mutant pancreatic cancer.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024 Aug 31;15(4):2002-2005. doi: 10.21037/jgo-24-255. Epub 2024 Aug 5. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39279949 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Exploring the Role of CBX3 as a Potential Therapeutic Target in Lung Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Aug 30;16(17):3026. doi: 10.3390/cancers16173026. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39272883 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effector Binding Sequentially Alters KRAS Dimerization on the Membrane: New Insights Into RAS-Mediated RAF Activation.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Oct;11(38):e2401530. doi: 10.1002/advs.202401530. Epub 2024 Aug 13. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 39138901 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

