Multifunctionalized carbon-fiber-reinforced polyetheretherketone implant for rapid osseointegration under infected environment
- PMID: 36606257
- PMCID: PMC9803906
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2022.12.016
Multifunctionalized carbon-fiber-reinforced polyetheretherketone implant for rapid osseointegration under infected environment
Abstract
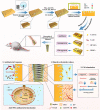
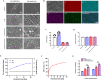
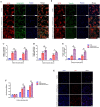
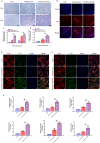
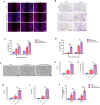
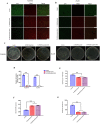
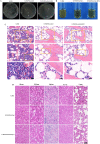
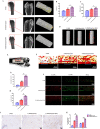
Carbon fiber reinforced polyetheretherketone (CFRPEEK) possesses a similar elastic modulus to that of human cortical bone and is considered as a promising candidate to replace metallic implants. However, the bioinertness and deficiency of antibacterial activities impede its application in orthopedic and dentistry. In this work, titanium plasma immersion ion implantation (Ti-PIII) is applied to modify CFRPEEK, achieving unique multi-hierarchical nanostructures and active sites on the surface. Then, hybrid polydopamine (PDA)@ZnO-EDN1 nanoparticles (NPs) are introduced to construct versatile surfaces with improved osteogenic and angiogenic properties and excellent antibacterial properties. Our study established that the modified CFRPEEK presented favorable stability and cytocompatibility. Compared with bare CFRPEEK, improved osteogenic differentiation of rat mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) and vascularization of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) are found on the functionalized surface due to the zinc ions and EDN1 releasing. In vitro bacteriostasis assay confirms that hybrid PDA@ZnO NPs on the functionalized surface provided an effective antibacterial effect. Moreover, the rat infected model corroborates the enhanced antibiosis and osteointegration of the functionalized CFRPEEK. Our findings indicate that the multilevel nanostructured PDA@ZnO-EDN1 coated CFRPEEK with enhanced antibacterial, angiogenic, and osteogenic capacity has great potential as an orthopedic/dental implant material for clinical application.
Keywords: Antibacterial activity; Nanopores; Osteogenic activity; Polyetheretherketone; Vascularization.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Multilevel surface engineering of nanostructured TiO2 on carbon-fiber-reinforced polyetheretherketone.Biomaterials. 2014 Jul;35(22):5731-40. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.04.003. Epub 2014 Apr 22. Biomaterials. 2014. PMID: 24767786
-
Enhanced osteogenic and selective antibacterial activities on micro-/nano-structured carbon fiber reinforced polyetheretherketone.J Mater Chem B. 2016 May 7;4(17):2944-2953. doi: 10.1039/c6tb00268d. Epub 2016 Apr 18. J Mater Chem B. 2016. PMID: 32262972
-
A carboxymethyl chitosan and peptide-decorated polyetheretherketone ternary biocomposite with enhanced antibacterial activity and osseointegration as orthopedic/dental implants.J Mater Chem B. 2016 Mar 14;4(10):1878-1890. doi: 10.1039/c5tb02782a. Epub 2016 Feb 22. J Mater Chem B. 2016. PMID: 32263065
-
Selective responses of human gingival fibroblasts and bacteria on carbon fiber reinforced polyetheretherketone with multilevel nanostructured TiO2.Biomaterials. 2016 Mar;83:207-18. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2016.01.001. Epub 2016 Jan 4. Biomaterials. 2016. PMID: 26774566
-
Application of biomolecules modification strategies on PEEK and its composites for osteogenesis and antibacterial properties.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2022 Jul;215:112492. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2022.112492. Epub 2022 Apr 12. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2022. PMID: 35430485 Review.
Cited by
-
Overview of strategies to improve the antibacterial property of dental implants.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Sep 27;11:1267128. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1267128. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37829564 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of nanoparticles as surface modifiers of dental implants for revascularization/regeneration of bone.BMC Oral Health. 2024 Oct 4;24(1):1175. doi: 10.1186/s12903-024-04966-4. BMC Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 39367468 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influencing factors and evaluation methods for early stability of immediate implant.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024 Feb 28;49(2):305-311. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2024.230244. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024. PMID: 38755727 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese, English.
-
A microenvironment responsive polyetheretherketone implant with antibacterial and osteoimmunomodulatory properties facilitates osseointegration.Bioact Mater. 2024 Sep 25;43:273-291. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2024.09.017. eCollection 2025 Jan. Bioact Mater. 2024. PMID: 39399839 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang S., Yang Y., Li Y., Shi J., Zhou J., Zhang L., Deng Y., Yang W. Strontium/adiponectin co-decoration modulates the osteogenic activity of nano-morphologic polyetheretherketone implant. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces. 2019;176:38–46. - PubMed
-
- Lu T., Li J., Qian S., Cao H., Ning C., Liu X. Enhanced osteogenic and selective antibacterial activities on micro-/nano-structured carbon fiber reinforced polyetheretherketone. J. Mater. Chem. B. 2016;4(17):2944–2953. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

