Retinal Degeneration Animal Models in Bardet-Biedl Syndrome and Related Ciliopathies
- PMID: 36596648
- PMCID: PMC9808547
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a041303
Retinal Degeneration Animal Models in Bardet-Biedl Syndrome and Related Ciliopathies
Abstract
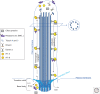
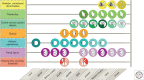
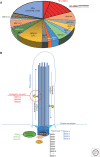
Retinal degeneration due to photoreceptor ciliary-related proteins dysfunction accounts for more than 25% of all inherited retinal dystrophies. The cilium, being an evolutionarily conserved and ubiquitous organelle implied in many cellular functions, can be investigated by way of many models from invertebrate models to nonhuman primates, all these models have massively contributed to the pathogenesis understanding of human ciliopathies. Taking the Bardet-Biedl syndrome (BBS) as an emblematic example as well as other related syndromic ciliopathies, the contribution of a wide range of models has enabled to characterize the role of the BBS proteins in the archetypical cilium but also at the level of the connecting cilium of the photoreceptors. There are more than 24 BBS genes encoding for proteins that form different complexes such as the BBSome and the chaperone proteins complex. But how they lead to retinal degeneration remains a matter of debate with the possible accumulation of proteins in the inner segment and/or accumulation of unwanted proteins in the outer segment that cannot return in the inner segment machinery. Many BBS proteins (but not the chaperonins for instance) can be modeled in primitive organisms such as Paramecium, Chlamydomonas reinardtii, Trypanosoma brucei, and Caenorhabditis elegans These models have enabled clarifying the role of a subset of BBS proteins in the primary cilium as well as their relations with other modules such as the intraflagellar transport (IFT) module, the nephronophthisis (NPHP) module, or the Meckel-Gruber syndrome (MKS)/Joubert syndrome (JBTS) module mostly involved with the transition zone of the primary cilia. Assessing the role of the primary cilia structure of the connecting cilium of the photoreceptor cells has been very much studied by way of zebrafish modeling (Danio rerio) as well as by a plethora of mouse models. More recently, large animal models have been described for three BBS genes and one nonhuman primate model in rhesus macaque for BBS7 In completion to animal models, human cell models can now be used notably thanks to gene editing and the use of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). All these models are not only important for pathogenesis understanding but also very useful for studying therapeutic avenues, their pros and cons, especially for gene replacement therapy as well as pharmacological triggers.
Copyright © 2023 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; all rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Qualitative evidence synthesis informing our understanding of people's perceptions and experiences of targeted digital communication.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Oct 23;10(10):ED000141. doi: 10.1002/14651858.ED000141. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31643081 Free PMC article.
-
Healthcare workers' informal uses of mobile phones and other mobile devices to support their work: a qualitative evidence synthesis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Aug 27;8(8):CD015705. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015705.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39189465 Free PMC article.
-
Defining the optimum strategy for identifying adults and children with coeliac disease: systematic review and economic modelling.Health Technol Assess. 2022 Oct;26(44):1-310. doi: 10.3310/ZUCE8371. Health Technol Assess. 2022. PMID: 36321689 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions to reduce harm from continued tobacco use.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Oct 13;10(10):CD005231. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005231.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27734465 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Usher syndrome proteins ADGRV1 (USH2C) and CIB2 (USH1J) interact and share a common interactome containing TRiC/CCT-BBS chaperonins.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Jun 22;11:1199069. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1199069. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37427378 Free PMC article.
-
Another Swim in the Extensive Pool of Zebrafish Research.Biomedicines. 2024 Feb 29;12(3):546. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12030546. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38540159 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aleman TS, O'Neil EC, O'Connor K, Jiang YY, Aleman IA, Bennett J, Morgan JIW, Toussaint BW. 2021. Bardet–Biedl syndrome-7 (BBS7) shows treatment potential and a cone-rod dystrophy phenotype that recapitulates the non-human primate model. Ophthalmic Genet 42: 252–265. 10.1080/13816810.2021.1888132 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Azari AA, Aleman TS, Cideciyan AV, Schwartz SB, Windsor EAM, Sumaroka A, Cheung AY, Steinberg JD, Roman AJ, Stone EM, et al. 2006. Retinal disease expression in Bardet–Biedl syndrome-1 (BBS1) is a spectrum from maculopathy to retina-wide degeneration. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 47: 5004–5010. 10.1167/iovs.06-0517 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
