Molecular and biological characteristics of a novel chrysovirus infecting the fungus phytopathogenic Setosphaeria turcica f.sp. sorghi
- PMID: 36596382
- PMCID: PMC10194276
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virusres.2022.199037
Molecular and biological characteristics of a novel chrysovirus infecting the fungus phytopathogenic Setosphaeria turcica f.sp. sorghi
Abstract
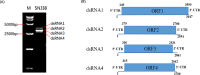
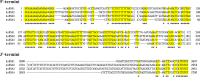
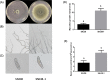
A new double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) virus has been identified in the filamentous fungus Setosphaeria turcica f.sp. sorghi, whose genome consists of four segments (dsRNA1-4). Each dsRNA carries single open reading frame (ORF) flanked by 5' and 3' untranslated regions (UTRs) containing strictly conserved termini. The putative protein encoded by dsRNA1 showed 80.50% identity to the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) of the most closely related virus, Alternaria alternata chrysovirus 1 (AaCV1), belonging to the Chrysoviridae. dsRNA2 encodes the putative coat protein, while dsRNA3 and dsRNA4 respectively encode the hypothetical proteins of unknown functions. Phylogenetic analysis based on the RdRp protein indicated the virus clustered with members of the genus Betachrysovirus in the family Chrysoviridae. Based on the dsRNA profile, amino acid sequence comparisons, and phylogenetic analyses, the mycovirus is thought to be a new member of the family Chrysoviridae and designated as Setosphaeria turcica chrysovirus 1 (StCV1). Moreover, obvious differences were observed in the colony, mycelial and spore morphology between StCV1-infected and virus-cured strains of S. turcica f.sp. sorghi. StCV1 infection strongly reduced colony growth rate, spore production ability and virulence on host fungus. To our knowledge, this is the first report about mycovirus infecting S. turcica f.sp. sorghi and also the first chrysovirus infecting S. turcica.
Keywords: Chrysovirus; Genetic diversity; Setosphaeria turcica chrysovirus 1; Setosphaeria turcica f.sp. sorghi.
Copyright © 2022. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Interaction between Hypovirulence-Associated Chrysoviruses and Their Host Fusarium Species.Viruses. 2024 Feb 5;16(2):253. doi: 10.3390/v16020253. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38400029 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Four distinct isolates of a novel polymycovirus identified in Setosphaeria turcica.Arch Virol. 2023 Jun 23;168(7):189. doi: 10.1007/s00705-023-05819-1. Arch Virol. 2023. PMID: 37351692
-
Complete genome sequence of a novel chrysovirus infecting Aspergillus terreus.Arch Virol. 2023 Jul 20;168(8):209. doi: 10.1007/s00705-023-05839-x. Arch Virol. 2023. PMID: 37474811
-
Identification and sequence determination of a new chrysovirus infecting the phytopathogenic fungus Dothistroma septosporum.Arch Virol. 2023 Apr 18;168(5):144. doi: 10.1007/s00705-023-05768-9. Arch Virol. 2023. PMID: 37071213 Free PMC article.
-
Chrysoviruses in Magnaporthe oryzae.Viruses. 2018 Dec 8;10(12):697. doi: 10.3390/v10120697. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 30544784 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Fungal Viruses Unveiled: A Comprehensive Review of Mycoviruses.Viruses. 2023 May 19;15(5):1202. doi: 10.3390/v15051202. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 37243288 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Interaction between Hypovirulence-Associated Chrysoviruses and Their Host Fusarium Species.Viruses. 2024 Feb 5;16(2):253. doi: 10.3390/v16020253. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38400029 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Darissa O., Willingmann P., Schäfer W., Adam G. A novel double-stranded RNA mycovirus from Fusarium graminearum: nucleic acid sequence and genomic structure. Arch. Virol. 2011;156:647–658. - PubMed
-
- Fuke K., Takeshita K., Aoki N., Fukuhara T., Egusa M., Kodama M., Moriyama H. The presence of double-stranded RNAs in Alternaria alternata Japanese pear pathotype is associated with its morphological changes. J. Gener. Plant Pathol. 2011;77:248–252.
-
- Gao Z., Cai L., Liu M., Wang X., Yang J., An H., Deng Q., Zhang S., Fang S. A novel previously undescribed fusarivirus from the phytopathogenic fungus Setosphaeria turcica. Arch. Virol. 2021;166:665–669. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

