The effect of desensitizing agents on the bond strength of dentin bonding agents: A systematic review
- PMID: 36591577
- PMCID: PMC9795680
- DOI: 10.4103/jcd.jcd_248_21
The effect of desensitizing agents on the bond strength of dentin bonding agents: A systematic review
Abstract
Background: Dentinal hypersensitivity (DH) is a common dental problem and is treated non-invasively using topical application of various desensitizing agents. When there is loss of tooth structure or tooth preparation is to be followed by a bonded restoration, it requires application of dentin bonding agent. However, the effect of desensitizers on bond strength is still controversial.
Aim and objective: To evaluate the influence of different desensitizing agents on the bond strength of the dentin bonding agents.
Methods and materials: PICO strategy was used to formulate the research question. In-vitro studies conducted on human teeth to evaluate the bond strength of dentin bonding agent following the application of desensitizing agent were included. Electronic databases PubMed and Cochrane and google scholar were searched using search terms alone or in combination from the year 2010 till 2020. Search was conducted using the key words and MeSH terms (hypersensitivity, bond strength, dental adhesives, dentin bonding agents). The title and abstract were read to verify the inclusion and exclusion criteria and if further any details required, full article was accessed to check the criteria and then included or excluded. Data extraction was done using a customized data extraction form. The risk of bias was evaluated using modified Cochrane Collaboration Quality Assessment tool.
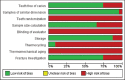
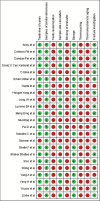
Results: Total no of studies identified in the search were 146, after scrutiny 23 articles were eligible to be included in this study. Out of 23 articles, 17 articles were of medium bias and 6 articles were of high risk after risk of bias assessment.
Conclusion: According to the various articles included in this study, GLUMA and 8.0%Arginine and CaCO3 when used as desensitizing agents along with different bonding agents, were found to be highly compatible without interfering with the bond strength of the dentin adhesives.
Keywords: Bond strength; Bonding agent; desensitiser; hypersensitivity.
Copyright: © 2022 Journal of Conservative Dentistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Brannstrom M. Sensitivity of dentine. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Path. 1996;21:517–26. - PubMed
-
- Pashley DH, Livingston MJ, Reeder OW, Horner J. Effects of the degree of tubule occlusion on the permeability of human dentin in-vitro. Arch Oral Biol. 1978;20:1127–33. - PubMed
-
- Susin AH, Vasconcellos WA, Saad JR, Oliveira Junior OB. Tensile bond strength of self-etching versus total-etching adhesive systems under different dentinal substrate conditions. Braz Oral Res. 2007;21:81–6. - PubMed
-
- Kobler A, Schaller HG, Gernhardt CR. Effects of the desensitizing agents Gluma and Hyposen on the tensile bond strength of dentin adhesives Am J Dent. 2008;21:388–92. - PubMed
-
- Aranha AC, Siqueira Junior Ade S, Cavalcante LM, Pimenta LA, Marchi GM. Microtensile bond strengths of composite to dentin treated with desensitizer products. J Adhes Dent. 2006;8:85–90. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources