The role of the stria vascularis in neglected otologic disease
- PMID: 36584545
- PMCID: PMC9840708
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heares.2022.108682
The role of the stria vascularis in neglected otologic disease
Abstract
The stria vascularis (SV) has been shown to play a critical role in the pathogenesis of many diseases associated with sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL), including age-related hearing loss (ARHL), noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL), hereditary hearing loss (HHL), and drug-induced hearing loss (DIHL), among others. There are a number of other disorders of hearing loss that may be relatively neglected due to being underrecognized, poorly understood, lacking robust diagnostic criteria or effective treatments. A few examples of these diseases include autoimmune inner ear disease (AIED) and/or autoinflammatory inner ear disease (AID), Meniere's disease (MD), sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSNHL), and cytomegalovirus (CMV)-related hearing loss (CRHL). Although these diseases may often differ in etiology, there have been recent studies that support the involvement of the SV in the pathogenesis of many of these disorders. We strive to highlight a few prominent examples of these frequently neglected otologic diseases and illustrate the relevance of understanding SV composition, structure and function with regards to these disease processes. In this study, we review the physiology of the SV, lay out the importance of these neglected otologic diseases, highlight the current literature regarding the role of the SV in these disorders, and discuss the current strategies, both approved and investigational, for management of these disorders.
Keywords: Autoimmune inner ear disease (AIED); Autoinflammatory inner ear disease (AID); Cytomegalovirus-related hearing loss (CRHL); Meniere's disease (MD); Stria vascularis (SV); Sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSNHL).
Published by Elsevier B.V.
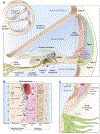
Figures

Similar articles
-
Repurposable Drugs That Interact with Steroid Responsive Gene Targets for Inner Ear Disease.Biomolecules. 2022 Nov 5;12(11):1641. doi: 10.3390/biom12111641. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36358991 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of common stria vascularis cellular alteration in sensorineural hearing loss based on ScRNA-seq.BMC Genomics. 2024 Feb 27;25(1):213. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10122-7. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38413848 Free PMC article.
-
Noncoding Microdeletion in Mouse Hgf Disrupts Neural Crest Migration into the Stria Vascularis, Reduces the Endocochlear Potential, and Suggests the Neuropathology for Human Nonsyndromic Deafness DFNB39.J Neurosci. 2020 Apr 8;40(15):2976-2992. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2278-19.2020. Epub 2020 Mar 9. J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32152201 Free PMC article.
-
Animal models of inner ear vascular disturbances.Am J Otolaryngol. 1986 Mar-Apr;7(2):130-9. doi: 10.1016/s0196-0709(86)80042-4. Am J Otolaryngol. 1986. PMID: 3515984 Review.
-
Biologics for Immune-Mediated Sensorineural Hearing Loss.Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2021 Aug;54(4):803-813. doi: 10.1016/j.otc.2021.05.005. Epub 2021 Jun 10. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2021. PMID: 34119332 Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging Mechanisms in the Pathogenesis of Menière's Disease: Evidence for the Involvement of Ion Homeostatic or Blood-Labyrinthine Barrier Dysfunction in Human Temporal Bones.Otol Neurotol. 2023 Dec 1;44(10):1057-1065. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000004016. Epub 2023 Sep 20. Otol Neurotol. 2023. PMID: 37733989 Free PMC article.
-
A critical evaluation of "leakage" at the cochlear blood-stria-barrier and its functional significance.Front Mol Neurosci. 2024 Feb 29;17:1368058. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2024.1368058. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38486963 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dissection of Adult Mouse Stria Vascularis for Single-Nucleus Sequencing or Immunostaining.J Vis Exp. 2023 Apr 21;(194):10.3791/65254. doi: 10.3791/65254. J Vis Exp. 2023. PMID: 37154552 Free PMC article.
-
The Stria Vascularis: Renewed Attention on a Key Player in Age-Related Hearing Loss.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 15;25(10):5391. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105391. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791427 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ABCC1 deficiency potentiated noise-induced hearing loss in mice by impairing cochlear antioxidant capacity.Redox Biol. 2024 Aug;74:103218. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103218. Epub 2024 Jun 1. Redox Biol. 2024. PMID: 38870779 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adachi N, Yoshida T, Nin F, Ogata G, Yamaguchi S, Suzuki T, Komune S, Hisa Y, Hibino H, Kurachi Y, 2013. The mechanism underlying maintenance of the endocochlear potential by the K+ transport system in fibrocytes of the inner ear. J Physiol 591(18), 4459–4472. 10.1113/jphysiol.2013.258046. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Andrianakis A, Moser U, Kiss P, Holzmeister C, Andrianakis D, Tomazic PV, Wolf A, Graupp M, 2022. Comparison of two different intratympanic corticosteroid injection protocols as salvage treatments for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 279(2), 609–618. 10.1007/s00405-021-06676-x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

