N6-methyladenosine modification of viral RNA and its role during the recognition process of RIG-I-like receptors
- PMID: 36582239
- PMCID: PMC9792670
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1031200
N6-methyladenosine modification of viral RNA and its role during the recognition process of RIG-I-like receptors
Abstract
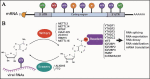
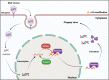
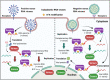
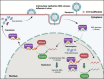
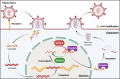
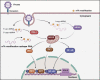
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is the most abundant RNA chemical modification in eukaryotes and is also found in the RNAs of many viruses. In recent years, m6A RNA modification has been reported to have a role not only in the replication of numerous viruses but also in the innate immune escape process. In this review, we describe the viruses that contain m6A in their genomes or messenger RNAs (mRNAs), and summarize the effects of m6A on the replication of different viruses. We also discuss how m6A modification helps viral RNAs escape recognition by exogenous RNA sensors, such as retinoic acid-inducible gene I (RIG-I)-like receptors (RLRs), during viral invasion. Overall, the goal of our review is to summarize how m6A regulates viral replication and facilitates innate immune escape. Furthermore, we elaborate on the potential of m6A as a novel antiviral target.
Keywords: RIG-I-like receptors; innate immune escape; m6A; replication; viruses.
Copyright © 2022 Li, Guo, Qi and Liao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nonsegmented Negative-Sense RNA Viruses Utilize N6-Methyladenosine (m6A) as a Common Strategy To Evade Host Innate Immunity.J Virol. 2021 Apr 12;95(9):e01939-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01939-20. Print 2021 Apr 12. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 33536170 Free PMC article.
-
N6-Methyladenosine modification of hepatitis B and C viral RNAs attenuates host innate immunity via RIG-I signaling.J Biol Chem. 2020 Sep 11;295(37):13123-13133. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.014260. Epub 2020 Jul 27. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32719095 Free PMC article.
-
N6-methyladenosine modification enables viral RNA to escape recognition by RNA sensor RIG-I.Nat Microbiol. 2020 Apr;5(4):584-598. doi: 10.1038/s41564-019-0653-9. Epub 2020 Feb 3. Nat Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32015498 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Viral Infection by the RNA Modification N6-Methyladenosine.Annu Rev Virol. 2019 Sep 29;6(1):235-253. doi: 10.1146/annurev-virology-092818-015559. Epub 2019 Jul 5. Annu Rev Virol. 2019. PMID: 31283446 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sensing viral invasion by RIG-I like receptors.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2014 Aug;20:131-8. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2014.05.011. Epub 2014 Jun 23. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24968321 Review.
References
-
- Bokar JA, Rath-Shambaugh ME, Ludwiczak R, Narayan P, Rottman F. Characterization and partial purification of mRNA N6-adenosine methyltransferase from HeLa cell nuclei. internal mRNA methylation requires a multisubunit complex. J Biol Chem (1994) 269(26):17697–704. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9258(17)32497-3 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

