Development of a simple multiple mutation detection system using seed-coat flavonoid pigments in irradiated Arabidopsis M1 plants
- PMID: 36577797
- PMCID: PMC9797493
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-26989-z
Development of a simple multiple mutation detection system using seed-coat flavonoid pigments in irradiated Arabidopsis M1 plants
Abstract
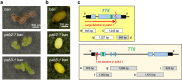
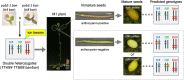
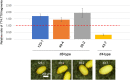
Ionizing radiation induces genetic variations in plants, which makes it useful for plant breeding. A theory that the induced mutations occur randomly in the genome has long been accepted, but is now controversial. Nevertheless, a comparative analysis of the mutations at multiple loci has not been conducted using irradiated M1 genomes that contain all types of mutations. In this study, we identified Arabidopsis mutants (pab2 and pab3) in a mutagenized population of an anthocyanin-positive seed mutant (ban). Both pab2 and pab3 were revealed to be double mutants (tt4 ban and tt8 ban, respectively) that produced similar anthocyanin-less immature seeds, but differentially colored mature seeds. These features enabled the seed color-based detection of de novo M1 mutations in TT4 or TT8 following the irradiation of double heterozygous plants (TT4/tt4 TT8/tt8 ban/ban). Most of the irradiated double heterozygous plants produced anthocyanin-positive immature seeds, but 19 plants produced anthocyanin-less immature seeds. Of these 19 mutants, 2 and 17 exhibited tt4- and tt8-type mature seed coloration, respectively. The molecular analysis of the seed coat DNA from randomly selected anthocyanin-less seeds detected mutations at the locus predicted on the basis of the phenotype. Thus, the simple system developed in this study can reliably detect radiation-induced mutations at multiple loci in irradiated Arabidopsis M1 plants.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Arabidopsis pab1, a mutant with reduced anthocyanins in immature seeds from banyuls, harbors a mutation in the MATE transporter FFT.Plant Mol Biol. 2016 Jan;90(1-2):7-18. doi: 10.1007/s11103-015-0389-8. Epub 2015 Nov 26. Plant Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26608698
-
BANYULS, a novel negative regulator of flavonoid biosynthesis in the Arabidopsis seed coat.Plant J. 1997 Feb;11(2):289-99. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.1997.11020289.x. Plant J. 1997. PMID: 9076994
-
TT8 controls its own expression in a feedback regulation involving TTG1 and homologous MYB and bHLH factors, allowing a strong and cell-specific accumulation of flavonoids in Arabidopsis thaliana.Plant J. 2006 Jun;46(5):768-79. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02733.x. Plant J. 2006. PMID: 16709193
-
Evolutionary studies of the bHLH transcription factors belonging to MBW complex: their role in seed development.Ann Bot. 2023 Nov 23;132(3):383-400. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcad097. Ann Bot. 2023. PMID: 37467144 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Flavonoids and the regulation of seed size in Arabidopsis.Biochem Soc Trans. 2014 Apr;42(2):364-9. doi: 10.1042/BST20140040. Biochem Soc Trans. 2014. PMID: 24646245 Review.
Cited by
-
Genomic view of heavy-ion-induced deletions associated with distribution of essential genes in Arabidopsis thaliana.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Apr 17;15:1352564. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1352564. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38693931 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nakagawa, H. In Induced Plant Mutations in the Genomic Era (ed Shu, Q. Y.) 51–58 (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, 2009).
-
- Jo YD, Kim J-B. Frequency and spectrum of radiation-induced mutations revealed by whole-genome sequencing analysis of plants. Quantum Beam Sci. 2019;3:7. doi: 10.3390/qubs3020007. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

