Advances in NURR1-Regulated Neuroinflammation Associated with Parkinson's Disease
- PMID: 36555826
- PMCID: PMC9788636
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms232416184
Advances in NURR1-Regulated Neuroinflammation Associated with Parkinson's Disease
Abstract
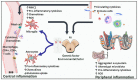
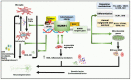
Neuroinflammation plays a crucial role in the progression of neurodegenerative disorders, particularly Parkinson's disease (PD). Glial cell activation and subsequent adaptive immune involvement are neuroinflammatory features in familial and idiopathic PD, resulting in the death of dopaminergic neuron cells. An oxidative stress response, inflammatory mediator production, and immune cell recruitment and activation are all hallmarks of this activation, leading to chronic neuroinflammation and progressive neurodegeneration. Several studies in PD patients' cerebrospinal fluid and peripheral blood revealed alterations in inflammatory markers and immune cell populations that may lead to or exacerbate neuroinflammation and perpetuate the neurodegenerative process. Most of the genes causing PD are also expressed in astrocytes and microglia, converting their neuroprotective role into a pathogenic one and contributing to disease onset and progression. Nuclear receptor-related transcription factor 1 (NURR1) regulates gene expression linked to dopaminergic neuron genesis and functional maintenance. In addition to playing a key role in developing and maintaining neurotransmitter phenotypes in dopaminergic neurons, NURR1 agonists have been shown to reverse behavioral and histological abnormalities in animal PD models. NURR1 protects dopaminergic neurons from inflammation-induced degeneration, specifically attenuating neuronal death by suppressing the expression of inflammatory genes in microglia and astrocytes. This narrative review highlights the inflammatory changes in PD and the advances in NURR1-regulated neuroinflammation associated with PD. Further, we present new evidence that targeting this inflammation with a variety of potential NURR1 target therapy medications can effectively slow the progression of chronic neuroinflammation-induced PD.
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease; astrocytes; microglia; neuroinflammation; nuclear receptor-related transcription factor 1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protein kinase Cδ upregulation in microglia drives neuroinflammatory responses and dopaminergic neurodegeneration in experimental models of Parkinson's disease.Neurobiol Dis. 2016 Sep;93:96-114. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2016.04.008. Epub 2016 May 2. Neurobiol Dis. 2016. PMID: 27151770 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of the JAK/STAT Pathway Protects Against α-Synuclein-Induced Neuroinflammation and Dopaminergic Neurodegeneration.J Neurosci. 2016 May 4;36(18):5144-59. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4658-15.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27147665 Free PMC article.
-
Nurr1 promotes neurogenesis of dopaminergic neuron and represses inflammatory factors in the transwell coculture system of neural stem cells and microglia.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2018 Sep;24(9):790-800. doi: 10.1111/cns.12825. Epub 2018 Feb 15. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2018. PMID: 29450981 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroinflammation and Parkinson's Disease-From Neurodegeneration to Therapeutic Opportunities.Cells. 2022 Sep 17;11(18):2908. doi: 10.3390/cells11182908. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36139483 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of Toll-like receptors and neuroinflammation in Parkinson's disease.J Neuroinflammation. 2022 Jun 6;19(1):135. doi: 10.1186/s12974-022-02496-w. J Neuroinflammation. 2022. PMID: 35668422 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The role of Nurr1-miR-30e-5p-NLRP3 axis in inflammation-mediated neurodegeneration: insights from mouse models and patients' studies in Parkinson's disease.J Neuroinflammation. 2023 Nov 22;20(1):274. doi: 10.1186/s12974-023-02956-x. J Neuroinflammation. 2023. PMID: 37990334 Free PMC article.
-
NR4A2 as a Novel Target Gene for Developmental and Epileptic Encephalopathy: A Systematic Review of Related Disorders and Therapeutic Strategies.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 10;25(10):5198. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105198. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791237 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ferulic Acid reduces amyloid beta mediated neuroinflammation through modulation of Nurr1 expression in microglial cells.PLoS One. 2023 Aug 17;18(8):e0290249. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0290249. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37590236 Free PMC article.
-
Infectious Microorganisms Seen as Etiologic Agents in Parkinson's Disease.Life (Basel). 2023 Mar 16;13(3):805. doi: 10.3390/life13030805. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36983960 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein restriction during pregnancy alters Cdkn1c silencing, dopamine circuitry and offspring behaviour without changing expression of key neuronal marker genes.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 12;14(1):8528. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-59083-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38609446 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

