Vasopressin as a Possible Link between Sleep-Disturbances and Memory Problems
- PMID: 36555107
- PMCID: PMC9778878
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms232415467
Vasopressin as a Possible Link between Sleep-Disturbances and Memory Problems
Abstract
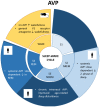
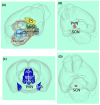
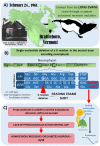
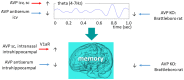
Normal biological rhythms, including sleep, are very important for a healthy life and their disturbance may induce-among other issues-memory impairment, which is a key problem of many psychiatric pathologies. The major brain center of circadian regulation is the suprachiasmatic nucleus, and vasopressin (AVP), which is one of its main neurotransmitters, also plays a key role in memory formation. In this review paper, we aimed to summarize our knowledge on the vasopressinergic connection between sleep and memory with the help of the AVP-deficient Brattleboro rat strain. These animals have EEG disturbances with reduced sleep and impaired memory-boosting theta oscillation and show memory impairment in parallel. Based upon human and animal data measuring AVP levels, haplotypes, and the administration of AVP or its agonist or antagonist via different routes (subcutaneous, intraperitoneal, intracerebroventricular, or intranasal), V1a receptors (especially of hippocampal origin) were implicated in the sleep-memory interaction. All in all, the presented data confirm the possible connective role of AVP between biological rhythms and memory formation, thus, supporting the importance of AVP in several psychopathological conditions.
Keywords: Brattleboro rat; EEG; circadian rhythm; memory; novel object recognition; sleep; vasopressin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Vasopressin-deficient rats show a reduced amplitude of the circadian sleep rhythm.Physiol Behav. 1989 Oct;46(4):759-62. doi: 10.1016/0031-9384(89)90364-8. Physiol Behav. 1989. PMID: 2602503
-
Vasopressin-deficient suprachiasmatic nucleus grafts re-instate circadian rhythmicity in suprachiasmatic nucleus-lesioned arrhythmic rats.Neuroscience. 1999 Mar;89(2):375-85. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(98)00300-5. Neuroscience. 1999. PMID: 10077320
-
The diurnal rhythm in vasopressin V1a receptor expression in the suprachiasmatic nucleus is not dependent on vasopressin.Endocrinology. 1993 Aug;133(2):585-90. doi: 10.1210/endo.133.2.8344200. Endocrinology. 1993. PMID: 8344200
-
Vasopressin in circadian function of SCN.J Biosci. 2020;45:140. J Biosci. 2020. PMID: 33361631 Review.
-
Vasopressin signaling at brain level controls stress hormone release: the vasopressin-deficient Brattleboro rat as a model.Amino Acids. 2015 Nov;47(11):2245-53. doi: 10.1007/s00726-015-2026-x. Epub 2015 Jun 23. Amino Acids. 2015. PMID: 26100541 Review.
Cited by
-
A dopamine D1-like receptor-specific agonist improves the survival of septic mice.iScience. 2024 Mar 27;27(4):109587. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109587. eCollection 2024 Apr 19. iScience. 2024. PMID: 38623339 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ikeda M., Matsuzaki T. Regulation of aquaporins by vasopressin in the kidney. Vitam. Horm. 2015;98:307–337. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

