Lipid Droplet-Associated Proteins Perilipin 1 and 2: Molecular Markers of Steatosis and Microvesicular Steatotic Foci in Chronic Hepatitis C
- PMID: 36555099
- PMCID: PMC9778710
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms232415456
Lipid Droplet-Associated Proteins Perilipin 1 and 2: Molecular Markers of Steatosis and Microvesicular Steatotic Foci in Chronic Hepatitis C
Abstract
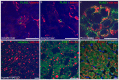
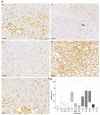
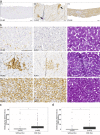
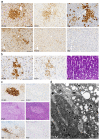
Chronic infection with hepatitis C (HCV) is a major risk factor in the development of cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Lipid metabolism plays a major role in the replication and deposition of HCV at lipid droplets (LDs). We have demonstrated the importance of LD-associated proteins of the perilipin family in steatotic liver diseases. Using a large collection of 231 human liver biopsies with HCV, perilipins 1 and 2 have been localized to LDs of hepatocytes that correlate with the degree of steatosis and specific HCV genotypes, but not significantly with the HCV viral load. Perilipin 1- and 2-positive microvesicular steatotic foci were observed in 36% of HCV liver biopsies, and also in chronic hepatitis B, autoimmune hepatitis and mildly steatotic or normal livers, but less or none were observed in normal livers of younger patients. Microvesicular steatotic foci did not frequently overlap with glycogenotic/clear cell foci as determined by PAS stain in serial sections. Steatotic foci were detected in all liver zones with slight architectural disarrays, as demonstrated by immunohistochemical glutamine synthetase staining of zone three, but without elevated Ki67-proliferation rates. In conclusion, microvesicular steatotic foci are frequently found in chronic viral hepatitis, but the clinical significance of these foci is so far not clear.
Keywords: PAT proteins; focal fatty change; hepatitis B virus (HBV); hepatitis C virus (HCV); non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).
Conflict of interest statement
B.K.S. has taken part in an advisory board of Bayer Healthcare concerning radiology of hepatocellular carcinoma. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Perilipin 5 alleviates HCV NS5A-induced lipotoxic injuries in liver.Lipids Health Dis. 2019 Apr 6;18(1):87. doi: 10.1186/s12944-019-1022-7. Lipids Health Dis. 2019. PMID: 30954078 Free PMC article.
-
Perilipin discerns chronic from acute hepatocellular steatosis.J Hepatol. 2014 Mar;60(3):633-42. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.11.007. Epub 2013 Nov 19. J Hepatol. 2014. PMID: 24269473
-
Clinicopathological features of hepatocellular carcinoma with fatty change: Tumors with macrovesicular steatosis have better prognosis and aberrant expression patterns of perilipin and adipophilin.Pathol Int. 2020 Apr;70(4):199-209. doi: 10.1111/pin.12889. Epub 2020 Jan 12. Pathol Int. 2020. PMID: 31930673
-
[Lipid droplet-associated proteins. Importance in steatosis, steatohepatitis and hepatocarcinogenesis].Pathologe. 2015 Nov;36 Suppl 2:146-52. doi: 10.1007/s00292-015-0082-3. Pathologe. 2015. PMID: 26400566 Review. German.
-
Pathophysiology of lipid droplet proteins in liver diseases.Exp Cell Res. 2016 Jan 15;340(2):187-92. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2015.10.021. Epub 2015 Oct 26. Exp Cell Res. 2016. PMID: 26515554 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lipid droplets in pathogen infection and host immunity.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024 Mar;45(3):449-464. doi: 10.1038/s41401-023-01189-1. Epub 2023 Nov 22. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024. PMID: 37993536 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Upregulation of Hepatic Glutathione S-Transferase Alpha 1 Ameliorates Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatosis by Degrading Fatty Acid Binding Protein 1.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 7;25(10):5086. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105086. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791126 Free PMC article.
-
Palmitic Acid Induces Oxidative Stress and Senescence in Human Brainstem Astrocytes, Downregulating Glutamate Reuptake Transporters-Implications for Obesity-Related Sympathoexcitation.Nutrients. 2024 Aug 26;16(17):2852. doi: 10.3390/nu16172852. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39275168 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic Liver Disease: Latest Research in Pathogenesis, Detection and Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 25;24(13):10633. doi: 10.3390/ijms241310633. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37445809 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

