53BP1: Keeping It under Control, Even at a Distance from DNA Damage
- PMID: 36553657
- PMCID: PMC9778356
- DOI: 10.3390/genes13122390
53BP1: Keeping It under Control, Even at a Distance from DNA Damage
Abstract
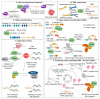
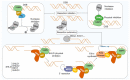
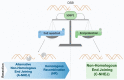
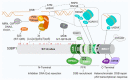
Double-strand breaks (DSBs) are toxic lesions that can be generated by exposure to genotoxic agents or during physiological processes, such as during V(D)J recombination. The repair of these DSBs is crucial to prevent genomic instability and to maintain cellular homeostasis. Two main pathways participate in repairing DSBs, namely, non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) and homologous recombination (HR). The P53-binding protein 1 (53BP1) plays a pivotal role in the choice of DSB repair mechanism, promotes checkpoint activation and preserves genome stability upon DSBs. By preventing DSB end resection, 53BP1 promotes NHEJ over HR. Nonetheless, the balance between DSB repair pathways remains crucial, as unscheduled NHEJ or HR events at different phases of the cell cycle may lead to genomic instability. Therefore, the recruitment of 53BP1 to chromatin is tightly regulated and has been widely studied. However, less is known about the mechanism regulating 53BP1 recruitment at a distance from the DNA damage. The present review focuses on the mechanism of 53BP1 recruitment to damage and on recent studies describing novel mechanisms keeping 53BP1 at a distance from DSBs.
Keywords: 53BP1; BRCA1; PARP inhibitors; double-strand break repair; homologous recombination; lamins; non-homologous end joining; shieldin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of repair pathway choice at two-ended DNA double-strand breaks.Mutat Res. 2017 Oct;803-805:51-55. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2017.07.011. Epub 2017 Jul 29. Mutat Res. 2017. PMID: 28781144 Review.
-
Roles for 53BP1 in the repair of radiation-induced DNA double strand breaks.DNA Repair (Amst). 2020 Sep;93:102915. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2020.102915. DNA Repair (Amst). 2020. PMID: 33087281 Review.
-
Roles for the DNA-PK complex and 53BP1 in protecting ends from resection during DNA double-strand break repair.J Radiat Res. 2020 Sep 8;61(5):718-726. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rraa053. J Radiat Res. 2020. PMID: 32779701 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multifaceted regulation and functions of 53BP1 in NHEJ‑mediated DSB repair (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2022 Jul;50(1):90. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2022.5145. Epub 2022 May 18. Int J Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35583003 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Double-strand break repair: 53BP1 comes into focus.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014 Jan;15(1):7-18. doi: 10.1038/nrm3719. Epub 2013 Dec 11. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24326623 Review.
Cited by
-
CSB and SMARCAL1 compete for RPA32 at stalled forks and differentially control the fate of stalled forks in BRCA2-deficient cells.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 May 22;52(9):5067-5087. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae154. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38416570 Free PMC article.
-
Decline of DNA damage response along with myogenic differentiation.Life Sci Alliance. 2023 Nov 22;7(2):e202302279. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202302279. Print 2024 Feb. Life Sci Alliance. 2023. PMID: 37993260 Free PMC article.
-
The flexible and iterative steps within the NHEJ pathway.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2023 Jul-Aug;180-181:105-119. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2023.05.001. Epub 2023 May 5. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37150451 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of p53 by the mitotic surveillance/stopwatch pathway: implications in neurodevelopment and cancer.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Sep 27;12:1451274. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1451274. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39398482 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IDR-targeting compounds suppress HPV genome replication via disruption of phospho-BRD4 association with DNA damage response factors.Mol Cell. 2024 Jan 18;84(2):202-220.e15. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2023.11.022. Epub 2023 Dec 15. Mol Cell. 2024. PMID: 38103559 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

