NAA60 (HAT4): the newly discovered bi-functional Golgi member of the acetyltransferase family
- PMID: 36539894
- PMCID: PMC9769039
- DOI: 10.1186/s13148-022-01402-8
NAA60 (HAT4): the newly discovered bi-functional Golgi member of the acetyltransferase family
Abstract
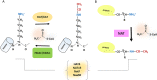
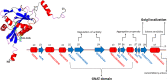
Chromatin structural organization, gene expression and proteostasis are intricately regulated in a wide range of biological processes, both physiological and pathological. Protein acetylation, a major post-translational modification, is tightly involved in interconnected biological networks, modulating the activation of gene transcription and protein action in cells. A very large number of studies describe the pivotal role of the so-called acetylome (accounting for more than 80% of the human proteome) in orchestrating different pathways in response to stimuli and triggering severe diseases, including cancer. NAA60/NatF (N-terminal acetyltransferase F), also named HAT4 (histone acetyltransferase type B protein 4), is a newly discovered acetyltransferase in humans modifying N-termini of transmembrane proteins starting with M-K/M-A/M-V/M-M residues and is also thought to modify lysine residues of histone H4. Because of its enzymatic features and unusual cell localization on the Golgi membrane, NAA60 is an intriguing acetyltransferase that warrants biochemical and clinical investigation. Although it is still poorly studied, this review summarizes current findings concerning the structural hallmarks and biological role of this novel targetable epigenetic enzyme.
Keywords: Cancer; Epigenetics; Golgi; HAT4; Histone acetyltransferases; NAA60; NAT; NAT15; NatF; Protein acetylation; Protein post-translational modification.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An organellar nα-acetyltransferase, naa60, acetylates cytosolic N termini of transmembrane proteins and maintains Golgi integrity.Cell Rep. 2015 Mar 3;10(8):1362-74. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.01.053. Epub 2015 Feb 26. Cell Rep. 2015. PMID: 25732826
-
Molecular determinants of the N-terminal acetyltransferase Naa60 anchoring to the Golgi membrane.J Biol Chem. 2017 Apr 21;292(16):6821-6837. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.770362. Epub 2017 Feb 14. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28196861 Free PMC article.
-
HAT4, a Golgi apparatus-anchored B-type histone acetyltransferase, acetylates free histone H4 and facilitates chromatin assembly.Mol Cell. 2011 Oct 7;44(1):39-50. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.07.032. Mol Cell. 2011. PMID: 21981917
-
Recent insights into Histone Acetyltransferase-1: biological function and involvement in pathogenesis.Epigenetics. 2021 Aug;16(8):838-850. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2020.1827723. Epub 2020 Oct 4. Epigenetics. 2021. PMID: 33016232 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The key roles of the lysine acetyltransferases KAT6A and KAT6B in physiology and pathology.Drug Resist Updat. 2020 Dec;53:100729. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2020.100729. Epub 2020 Oct 7. Drug Resist Updat. 2020. PMID: 33130515 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

