The dynamics of three-dimensional chromatin organization and phase separation in cell fate transitions and diseases
- PMID: 36539553
- PMCID: PMC9768101
- DOI: 10.1186/s13619-022-00145-4
The dynamics of three-dimensional chromatin organization and phase separation in cell fate transitions and diseases
Abstract
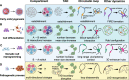
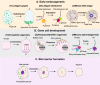
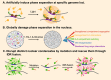
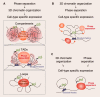
Cell fate transition is a fascinating process involving complex dynamics of three-dimensional (3D) chromatin organization and phase separation, which play an essential role in cell fate decision by regulating gene expression. Phase separation is increasingly being considered a driving force of chromatin folding. In this review, we have summarized the dynamic features of 3D chromatin and phase separation during physiological and pathological cell fate transitions and systematically analyzed recent evidence of phase separation facilitating the chromatin structure. In addition, we discuss current advances in understanding how phase separation contributes to physical and functional enhancer-promoter contacts. We highlight the functional roles of 3D chromatin organization and phase separation in cell fate transitions, and more explorations are required to study the regulatory relationship between 3D chromatin organization and phase separation. 3D chromatin organization (shown by Hi-C contact map) and phase separation are highly dynamic and play functional roles during early embryonic development, cell differentiation, somatic reprogramming, cell transdifferentiation and pathogenetic process. Phase separation can regulate 3D chromatin organization directly, but whether 3D chromatin organization regulates phase separation remains unclear.
Keywords: 3D chromatin organization; Cell fate transitions; Disease; Phase separation.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phase Separation: Direct and Indirect Driving Force for High-Order Chromatin Organization.Genes (Basel). 2023 Feb 15;14(2):499. doi: 10.3390/genes14020499. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36833426 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reprogramming of three-dimensional chromatin organization in the early embryo.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2023 Aug;81:102613. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2023.102613. Epub 2023 May 22. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2023. PMID: 37224641 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The influence of high-order chromatin state in the regulation of stem cell fate.Biochem Soc Trans. 2022 Dec 16;50(6):1809-1822. doi: 10.1042/BST20220763. Biochem Soc Trans. 2022. PMID: 36484643 Review.
-
Three-dimensional genome structure and function.MedComm (2020). 2023 Jul 8;4(4):e326. doi: 10.1002/mco2.326. eCollection 2023 Aug. MedComm (2020). 2023. PMID: 37426677 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phase Separation-Mediated Chromatin Organization and Dynamics: From Imaging-Based Quantitative Characterizations to Functional Implications.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 21;23(14):8039. doi: 10.3390/ijms23148039. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35887384 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hi-C, a chromatin 3D structure technique advancing the functional genomics of immune cells.Front Genet. 2024 Mar 22;15:1377238. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1377238. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 38586584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phase Separation of Chromatin Structure-related Biomolecules: A Driving Force for Epigenetic Regulations.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2024;25(7):553-566. doi: 10.2174/0113892037296216240301074253. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2024. PMID: 38551058 Review.
-
Long-range transcription factor binding sites clustered regions may mediate transcriptional regulation through phase-separation interactions in early human embryo.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2024 Sep 26;23:3514-3526. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2024.09.017. eCollection 2024 Dec. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2024. PMID: 39435341 Free PMC article.
-
Phase Separation: Direct and Indirect Driving Force for High-Order Chromatin Organization.Genes (Basel). 2023 Feb 15;14(2):499. doi: 10.3390/genes14020499. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36833426 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of long-range chromatin contacts, compartments and looping between mouse embryonic stem cells, lens epithelium and lens fibers.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2024 Apr 20;17(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s13072-024-00533-x. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2024. PMID: 38643244 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
- 2017YFA0102800/National Key Research and Development Program of China Stem Cell and Translational Research
- 31771639/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 31970811/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 32170798/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2018GZR110105007/Guangdong Regenerative Medicine and Health of Guangdong Laboratory Frontier Exploration Project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
