The MRN complex and topoisomerase IIIa-RMI1/2 synchronize DNA resection motor proteins
- PMID: 36529288
- PMCID: PMC9971906
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102802
The MRN complex and topoisomerase IIIa-RMI1/2 synchronize DNA resection motor proteins
Abstract
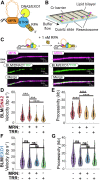
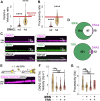
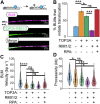
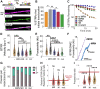
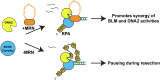
DNA resection-the nucleolytic processing of broken DNA ends-is the first step of homologous recombination. Resection is catalyzed by the resectosome, a multienzyme complex that includes bloom syndrome helicase (BLM), DNA2 or exonuclease 1 nucleases, and additional DNA-binding proteins. Although the molecular players have been known for over a decade, how the individual proteins work together to regulate DNA resection remains unknown. Using single-molecule imaging, we characterized the roles of the MRE11-RAD50-NBS1 complex (MRN) and topoisomerase IIIa (TOP3A)-RMI1/2 during long-range DNA resection. BLM partners with TOP3A-RMI1/2 to form the BTRR (BLM-TOP3A-RMI1/2) complex (or BLM dissolvasome). We determined that TOP3A-RMI1/2 aids BLM in initiating DNA unwinding, and along with MRN, stimulates DNA2-mediated resection. Furthermore, we found that MRN promotes the association between BTRR and DNA and synchronizes BLM and DNA2 translocation to prevent BLM from pausing during resection. Together, this work provides direct observation of how MRN and DNA2 harness the BTRR complex to resect DNA efficiently and how TOP3A-RMI1/2 regulates the helicase activity of BLM to promote efficient DNA repair.
Keywords: BLM; DNA curtains; DNA resection; DNA2; double-strand break; single molecule.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
DNA2 cooperates with the WRN and BLM RecQ helicases to mediate long-range DNA end resection in human cells.J Biol Chem. 2014 Sep 26;289(39):27314-27326. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.578823. Epub 2014 Aug 13. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25122754 Free PMC article.
-
BLM-DNA2-RPA-MRN and EXO1-BLM-RPA-MRN constitute two DNA end resection machineries for human DNA break repair.Genes Dev. 2011 Feb 15;25(4):350-62. doi: 10.1101/gad.2003811. Genes Dev. 2011. PMID: 21325134 Free PMC article.
-
Multifaceted role of the Topo IIIα-RMI1-RMI2 complex and DNA2 in the BLM-dependent pathway of DNA break end resection.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42(17):11083-91. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku803. Epub 2014 Sep 8. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 25200081 Free PMC article.
-
Making the best of the loose ends: Mre11/Rad50 complexes and Sae2 promote DNA double-strand break resection.DNA Repair (Amst). 2010 Dec 10;9(12):1283-91. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2010.09.015. Epub 2010 Nov 2. DNA Repair (Amst). 2010. PMID: 21050828 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA End Resection: Facts and Mechanisms.Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2016 Jun;14(3):126-130. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2016.05.002. Epub 2016 May 27. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2016. PMID: 27240470 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hyper-recombination in ribosomal DNA is driven by long-range resection-independent RAD51 accumulation.Nat Commun. 2024 Sep 6;15(1):7797. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-52189-6. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39242676 Free PMC article.
-
Resection of DNA double-strand breaks activates Mre11-Rad50-Nbs1- and Rad9-Hus1-Rad1-dependent mechanisms that redundantly promote ATR checkpoint activation and end processing in Xenopus egg extracts.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Apr 12;52(6):3146-3163. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae082. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38349040 Free PMC article.
-
RMI1 facilitates repair of ionizing radiation-induced DNA damage and maintenance of genomic stability.Cell Death Discov. 2023 Nov 25;9(1):426. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01726-1. Cell Death Discov. 2023. PMID: 38007566 Free PMC article.
-
Variation of Structure and Cellular Functions of Type IA Topoisomerases across the Tree of Life.Cells. 2024 Mar 21;13(6):553. doi: 10.3390/cells13060553. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38534397 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mathiasen D.P., Lisby M. Cell cycle regulation of homologous recombination in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2014;38:172–184. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

