Surveillance of the progression and assessment of treatment endpoints for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
- PMID: 36521452
- PMCID: PMC10029951
- DOI: 10.3350/cmh.2022.0401
Surveillance of the progression and assessment of treatment endpoints for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
Abstract
Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is an aggressive form of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) characterized by steatosis-associated inflammation and liver injury. Without effective treatment or management, NASH can have life-threatening outcomes. Evaluation and identification of NASH patients at risk for adverse outcomes are therefore important. Key issues in screening NASH patients are the assessment of advanced fibrosis, differentiation of NASH from simple steatosis, and monitoring of dynamic changes during follow-up and treatment. Currently, NASH staging and evaluation of the effectiveness for drugs still rely on pathological diagnosis, despite sample error issues and the subjectivity associated with liver biopsy. Optimizing the pathological assessment of liver biopsy samples and developing noninvasive surrogate methods for accessible, accurate, and safe evaluation are therefore critical. Although noninvasive methods including elastography, serum soluble biomarkers, and combined models have been implemented in the last decade, noninvasive diagnostic measurements are not widely applied in clinical practice. More work remains to be done in establishing cost-effective strategies both for screening for at-risk NASH patients and identifying changes in disease severity. In this review, we summarize the current state of noninvasive methods for detecting steatosis, steatohepatitis, and fibrosis in patients with NASH, and discuss noninvasive assessments for screening at-risk patients with a focus on the characteristics that should be monitored at follow-up.
Keywords: Disease progression; Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis; Noninvasive diagnosis; Risk stratification; Treatment efficacy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts to disclose.
Figures
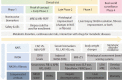
Similar articles
-
Noninvasive Assessment of Liver Disease in Patients With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.Gastroenterology. 2019 Apr;156(5):1264-1281.e4. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.12.036. Epub 2019 Jan 18. Gastroenterology. 2019. PMID: 30660725 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic modalities for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, and associated fibrosis.Hepatology. 2018 Jul;68(1):349-360. doi: 10.1002/hep.29721. Hepatology. 2018. PMID: 29222917 Free PMC article.
-
Liver fibrosis markers of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Jun 28;21(24):7427-35. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i24.7427. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26139988 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Noninvasive Evaluation of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.Semin Liver Dis. 2015 Aug;35(3):291-303. doi: 10.1055/s-0035-1562948. Epub 2015 Sep 17. Semin Liver Dis. 2015. PMID: 26378645 Review.
-
Noninvasive serum biomarkers for liver steatosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Current and future developments.Clin Mol Hepatol. 2023 Feb;29(Suppl):S150-S156. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2022.0362. Epub 2023 Jan 25. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 36696960 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Guideline for the Prevention and Treatment of Metabolic Dysfunction-associated Fatty Liver Disease (Version 2024).J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2024 Nov 28;12(11):955-974. doi: 10.14218/JCTH.2024.00311. Epub 2024 Nov 4. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 39544247 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Riazi K, Azhari H, Charette JH, Underwood FE, King JA, Afshar EE, et al. The prevalence and incidence of NAFLD worldwide: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;7:851–861. - PubMed
-
- Cotter TG, Rinella M. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease 2020: The state of the disease. Gastroenterology. 2020;158:1851–1864. - PubMed
-
- Sheka AC, Adeyi O, Thompson J, Hameed B, Crawford PA, Ikramuddin S. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: A review. JAMA. 2020;323:1175–1183. Erratum in: JAMA 2020;323:1619. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

