The alteration of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification at the transcriptome-wide level in response of heat stress in bovine mammary epithelial cells
- PMID: 36517742
- PMCID: PMC9749357
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-022-09067-6
The alteration of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification at the transcriptome-wide level in response of heat stress in bovine mammary epithelial cells
Abstract
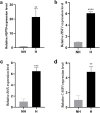
Background: Heat stress has a substantial negative economic impact on the dairy industry. N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is the most common internal RNA modification in eukaryotes and plays a key role in regulating heat stress response in animals. In dairy cows, however, this modification remains largely unexplored. Therefore, we examined the effects of heat stress on the m6A modification and gene expression in bovine mammary epithelial cells to elucidate the mechanism of heat stress response. In this study, Mammary alveolar cells-large T antigen (MAC-T) cells were incubated at 37 °C (non-heat stress group, NH) and 40 °C (heat stress group, H) for 2 hours, respectively. HSP70, HSF1, BAX and CASP3 were up regulated in H group compared with those in the NH group.
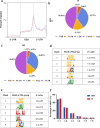
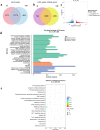
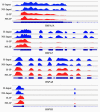
Results: Methylated RNA immunoprecipitation sequencing (MeRIP-seq) and RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) were conducted to identify m6A peaks and to produce gene expression data of MAC-T cells in the H and NH groups. In total, we identified 17,927 m6A peaks within 9355 genes in the H group, and 18,974 peaks within 9660 genes in the NH groups using MeRIP-seq. Compared with the NH group, 3005 significantly differentially enriched m6A peaks were identified, among which 1131 were up-regulated and 1874 were down-regulated. In addition, 1502 significantly differentially expressed genes were identified using RNA-seq, among which 796 were up-regulated and 706 were down-regulated in the H group compared to the NH group. Furthermore, 199 differentially expressed and synchronously differentially methylated genes were identified by conjoint analysis of the MeRIP-seq and RNA-seq data, which were subsequently divided into four groups: 47 hyper-up, 53 hyper-down, 59 hypo-up and 40 hypo-down genes. In addition, GO enrichment and KEGG analyses were used to analyzed the potential functions of the genes in each section.
Conclusion: The comparisons of m6A modification patterns and conjoint analyses of m6A modification and gene expression profiles suggest that m6A modification plays a critical role in the heat stress response by regulating gene expression.
Keywords: Heat stress; MAC-T; MeRIP-seq; N6-methyladenosine; m6A.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Transcriptome-wide methylated RNA immunoprecipitation sequencing profiling reveals m6A modification involved in response to heat stress in Apostichopus japonicus.BMC Genomics. 2024 Nov 11;25(1):1071. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10972-1. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39528936 Free PMC article.
-
Synchronous profiling of mRNA N6-methyladenosine modifications and mRNA expression in high-grade serous ovarian cancer: a pilot study.Sci Rep. 2024 May 7;14(1):10427. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-60975-x. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38714753 Free PMC article.
-
[Characteristics of N6-methyladenosine modification patterns in t(8;21) acute myeloid leukemia].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2022 May 20;42(5):690-697. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2022.05.09. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2022. PMID: 35673912 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
RNA m6A modifications in mammalian gametogenesis and pregnancy.Reproduction. 2022 Dec 2;165(1):R1-R8. doi: 10.1530/REP-22-0112. Print 2023 Jan 1. Reproduction. 2022. PMID: 36194446 Review.
-
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) Modification in Preeclampsia.Reprod Sci. 2023 Nov;30(11):3144-3152. doi: 10.1007/s43032-023-01250-8. Epub 2023 Jun 7. Reprod Sci. 2023. PMID: 37286755 Review.
Cited by
-
Changes in m6A in Steatotic Liver Disease.Genes (Basel). 2023 Aug 19;14(8):1653. doi: 10.3390/genes14081653. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37628704 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunotoxicity Evaluation of Trihalophenolic Disinfection By-Products in Mouse and Human Mononuclear Macrophage Systems: The Role of RNA Epitranscriptomic Modification in Mammalian Immunity.Environ Health Perspect. 2023 Dec;131(12):127023. doi: 10.1289/EHP11329. Epub 2023 Dec 29. Environ Health Perspect. 2023. PMID: 38157273 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome-wide N6-methyladenosine methylation profile of atherosclerosis in mice.BMC Genomics. 2023 Dec 14;24(1):774. doi: 10.1186/s12864-023-09878-1. BMC Genomics. 2023. PMID: 38097926 Free PMC article.
-
YTHDC1 m6A-dependent and m6A-independent functions converge to preserve the DNA damage response.EMBO J. 2024 Aug;43(16):3494-3522. doi: 10.1038/s44318-024-00153-x. Epub 2024 Jul 1. EMBO J. 2024. PMID: 38951610 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Analysis of YTH Domain-Containing Genes, Encoding m6A Reader and Their Response to Temperature Stresses and Yersinia ruckeri Infection in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss).Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 27;24(11):9348. doi: 10.3390/ijms24119348. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37298300 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

