High-quality and robust protein quantification in large clinical/pharmaceutical cohorts with IonStar proteomics investigation
- PMID: 36494494
- PMCID: PMC10673696
- DOI: 10.1038/s41596-022-00780-w
High-quality and robust protein quantification in large clinical/pharmaceutical cohorts with IonStar proteomics investigation
Abstract
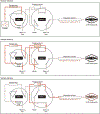
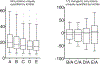
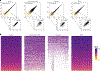
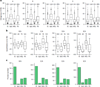
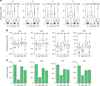
Robust, reliable quantification of large sample cohorts is often essential for meaningful clinical or pharmaceutical proteomics investigations, but it is technically challenging. When analyzing very large numbers of samples, isotope labeling approaches may suffer from substantial batch effects, and even with label-free methods, it becomes evident that low-abundance proteins are not reliably measured owing to unsufficient reproducibility for quantification. The MS1-based quantitative proteomics pipeline IonStar was designed to address these challenges. IonStar is a label-free approach that takes advantage of the high sensitivity/selectivity attainable by ultrahigh-resolution (UHR)-MS1 acquisition (e.g., 120-240k full width at half maximum at m/z = 200) which is now widely available on ultrahigh-field Orbitrap instruments. By selectively and accurately procuring quantitative features of peptides within precisely defined, very narrow m/z windows corresponding to the UHR-MS1 resolution, the method minimizes co-eluted interferences and substantially enhances signal-to-noise ratio of low-abundance species by decreasing noise level. This feature results in high sensitivity, selectivity, accuracy and precision for quantification of low-abundance proteins, as well as fewer missing data and fewer false positives. This protocol also emphasizes the importance of well-controlled, robust experimental procedures to achieve high-quality quantification across a large cohort. It includes a surfactant cocktail-aided sample preparation procedure that achieves high/reproducible protein/peptide recoveries among many samples, and a trapping nano-liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry strategy for sensitive and reproducible acquisition of UHR-MS1 peptide signal robustly across a large cohort. Data processing and quality evaluation are illustrated using an example dataset ( http://proteomecentral.proteomexchange.org ), and example results from pharmaceutical project and one clinical project (patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome) are shown. The complete IonStar pipeline takes ~1-2 weeks for a sample cohort containing ~50-100 samples.
© 2022. Springer Nature Limited.
Figures




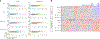
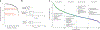
Similar articles
-
Ultra-High-Resolution IonStar Strategy Enhancing Accuracy and Precision of MS1-Based Proteomics and an Extensive Comparison with State-of-the-Art SWATH-MS in Large-Cohort Quantification.Anal Chem. 2021 Mar 23;93(11):4884-4893. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.0c05002. Epub 2021 Mar 9. Anal Chem. 2021. PMID: 33687211 Free PMC article.
-
An IonStar Experimental Strategy for MS1 Ion Current-Based Quantification Using Ultrahigh-Field Orbitrap: Reproducible, In-Depth, and Accurate Protein Measurement in Large Cohorts.J Proteome Res. 2017 Jul 7;16(7):2445-2456. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.7b00061. Epub 2017 May 25. J Proteome Res. 2017. PMID: 28412812 Free PMC article.
-
IonStar enables high-precision, low-missing-data proteomics quantification in large biological cohorts.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 May 22;115(21):E4767-E4776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1800541115. Epub 2018 May 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29743190 Free PMC article.
-
MS1 ion current-based quantitative proteomics: A promising solution for reliable analysis of large biological cohorts.Mass Spectrom Rev. 2019 Nov;38(6):461-482. doi: 10.1002/mas.21595. Epub 2019 Mar 28. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2019. PMID: 30920002 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tools for label-free peptide quantification.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2013 Mar;12(3):549-56. doi: 10.1074/mcp.R112.025163. Epub 2012 Dec 17. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2013. PMID: 23250051 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Systems Pharmacodynamic Model of Combined Gemcitabine and Trabectedin in Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Part II: Cell Cycle, DNA Damage Response, and Apoptosis Pathways.J Pharm Sci. 2024 Jan;113(1):235-245. doi: 10.1016/j.xphs.2023.10.036. Epub 2023 Nov 2. J Pharm Sci. 2024. PMID: 37918792 Free PMC article.
-
RESC14 and RESC8 cooperate to mediate RESC function and dynamics during trypanosome RNA editing.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Sep 9;52(16):9867-9885. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae561. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38967000 Free PMC article.
-
Tuning plant phenotypes by precise, graded downregulation of gene expression.Nat Biotechnol. 2023 Dec;41(12):1758-1764. doi: 10.1038/s41587-023-01707-w. Epub 2023 Mar 9. Nat Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36894598
-
Therapeutic TNF Inhibitors Exhibit Differential Levels of Efficacy in Accelerating Cutaneous Wound Healing.JID Innov. 2023 Nov 25;4(1):100250. doi: 10.1016/j.xjidi.2023.100250. eCollection 2024 Jan. JID Innov. 2023. PMID: 38226320 Free PMC article.
-
Systems pharmacodynamic model of combined gemcitabine and trabectedin in pancreatic cancer cells. Part I.Çô Effects on signal transduction pathways related to tumor growth.J Pharm Sci. 2024 Jan;113(1):214-227. doi: 10.1016/j.xphs.2023.10.030. Epub 2023 Oct 30. J Pharm Sci. 2024. PMID: 38498417 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

