A serological type II collagen neoepitope biomarker reflects cartilage breakdown in patients with osteoarthritis
- PMID: 36474766
- PMCID: PMC9718155
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ocarto.2021.100207
A serological type II collagen neoepitope biomarker reflects cartilage breakdown in patients with osteoarthritis
Abstract
Objectives: There is an unmet medical need for biomarkers in OA which can be applied in clinical drug development trials. The present study describes the development of a specific and robust assay measuring type II collagen degradation (T2CM) and discusses its potential as a noninvasive translational biomarker.
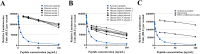
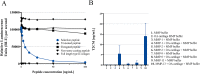
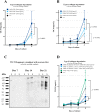
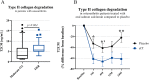
Methods: A type II collagen specific neoepitope (T2CM) was identified by mass spectrometry and monoclonal antibodies were raised towards the epitope, employed in a chemiluminescence immunoassay. T2CM was assessed in bovine cartilage explants with or without MMP-13 inhibitor, and explant supernatants were analyzed by Western blot. T2CM was measured in plasma samples from one study (n = 48 patients) where OA patients were referred to total knee replacement (TKR). Additionally, T2CM was quantified in serum from OA patients receiving salmon calcitonin treatment (sCT) (n = 50) compared to placebo (n = 57).
Results: The T2CM assay was technically robust (13/4 % inter/intra-variation) and specific for the type II collagen fragment cleaved by MMP-1 and -13. The MMP-13 inhibitor reduced the T2CM release from bovine cartilage explants receiving catabolic treatment. These results were confirmed by Western blot. In human end-stage OA patients (scheduled for TKR), the T2CM levels were elevated compared to moderate OA (p<0.004). The OA patients receiving sCT had lower levels of T2CM compared to placebo group after 1, 6, and 24 months of treatment (p = 0.0285, p = 0.0484, p = 0.0035).
Conclusions: To our knowledge, T2CM is the first technically robust serological biomarker assay which has shown biological relevance in ex vivo models and OA cohorts. This suggests that T2CM may have potential as a translational biomarker for cartilage degradation.
Keywords: Biomarker; Cartilage; Extracellular matrix; T2CM; Type II collagen.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The study was supported by The Danish Council for Technology and Innovation and The Danish National Advanced Technology Foundation. Morten A. Karsdal, Anne-Christine Bay-Jensen, Christian S. Thudium and Signe Holm Nielsen, Joseph Blair, and Line Mærsk are employees of Nordic Bioscience. Morten A. Karsdal holds stock in Nordic Bioscience. Sven Lindemann and Daniela Werkmann are employees of Merck. Solveig Skovlund Groen, Simon Francis Thomsen, Dovile Sinkeviciute, Patrik Önnerfjord, and Lars Arendt-Nielsen have no competing interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Selective enhancement of collagenase-mediated cleavage of resident type II collagen in cultured osteoarthritic cartilage and arrest with a synthetic inhibitor that spares collagenase 1 (matrix metalloproteinase 1).Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Mar;43(3):673-82. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200003)43:3<673::AID-ANR25>3.0.CO;2-8. Arthritis Rheum. 2000. PMID: 10728762
-
Biochemical markers identify influences on bone and cartilage degradation in osteoarthritis--the effect of sex, Kellgren-Lawrence (KL) score, body mass index (BMI), oral salmon calcitonin (sCT) treatment and diurnal variation.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2010 Jun 17;11:125. doi: 10.1186/1471-2474-11-125. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2010. PMID: 20565725 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Labisia pumila prevented osteoarthritis cartilage degeneration by attenuating joint inflammation and collagen breakdown in postmenopausal rat model.Inflammopharmacology. 2018 Oct;26(5):1207-1217. doi: 10.1007/s10787-018-0452-6. Epub 2018 Feb 19. Inflammopharmacology. 2018. PMID: 29460078
-
Oral salmon calcitonin reduces Lequesne's algofunctional index scores and decreases urinary and serum levels of biomarkers of joint metabolism in knee osteoarthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2006 Oct;54(10):3205-11. doi: 10.1002/art.22075. Arthritis Rheum. 2006. PMID: 17009253 Clinical Trial.
-
The effect of protease inhibitors on the induction of osteoarthritis-related biomarkers in bovine full-depth cartilage explants.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 24;10(4):e0122700. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0122700. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25909781 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Blood and urine biomarkers in osteoarthritis - an update on cartilage associated type II collagen and aggrecan markers.Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2022 Jan 1;34(1):54-60. doi: 10.1097/BOR.0000000000000845. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2022. PMID: 34652292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluating the inhibition of IL-17A and TNFα in a cartilage explant model cultured with Th17-derived cytokines.J Transl Autoimmun. 2024 Jan 7;8:100231. doi: 10.1016/j.jtauto.2024.100231. eCollection 2024 Jun. J Transl Autoimmun. 2024. PMID: 38292069 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular matrix turnover biomarkers reflect pharmacodynamic effects and treatment response of adalimumab in patients with axial spondyloarthritis-results from two randomized controlled trials.Arthritis Res Ther. 2023 Aug 25;25(1):157. doi: 10.1186/s13075-023-03132-5. Arthritis Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 37626399 Free PMC article.
-
A Highly Sensitive Biomarker of Type II Collagen C-Terminal Pro-Peptide Associated with Cartilage Formation.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 27;24(1):454. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010454. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36613894 Free PMC article.
-
The extracellular matrix alteration, implication in modulation of drug resistance mechanism: friends or foes?J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022 Sep 16;41(1):276. doi: 10.1186/s13046-022-02484-1. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 36114508 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

