Anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody Cetuximab displays potential anti-cancer activities in feline oral squamous cell carcinoma cell lines
- PMID: 36467642
- PMCID: PMC9712204
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2022.1040552
Anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody Cetuximab displays potential anti-cancer activities in feline oral squamous cell carcinoma cell lines
Abstract
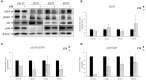
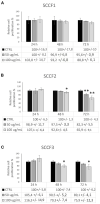
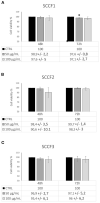
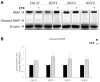
Feline oral squamous cell carcinoma (FOSCC) is a malignant tumor characterized by an aggressive behavior and poor prognosis, for which no fully effective therapies are available. Studies of comparative oncology suggest that epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) may be a therapeutic target in FOSCC, similarly to human head and neck SCC (HNSCC), where the use of anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody Cetuximab has entered the clinical practice. The aim of this study was to assess the efficacy of Cetuximab in three validated preclinical models of FOSCC (SCCF1, SCCF2, SCCF3). Sequencing of tyrosine kinase domain of EGFR in the cell lines revealed a wild-type genotype, excluding the presence of activating mutations. Western blotting experiments demonstrated that Cetuximab inhibited activation of EGFR and its downstream kinase Akt in SCCF1, SCCF2 and SCCF3 along with HNSCC cell line CAL 27 included as control. Importantly, CCK-8 and trypan blue exclusion assays revealed that treatment with Cetuximab caused a decrease in cell proliferation and cell viability in all cell lines, with a general dose- and time-dependent trend. Cell death induced by Cetuximab was associated with cleavage of PARP, indicating occurrence of apoptosis. Taken together, our data suggest that Cetuximab exerts potential anti-cancer activities in FOSCC, paving the way for future translational studies aimed at assessing its employment in the therapy of this lethal cancer of cats.
Keywords: Akt; Cetuximab; EGFR; cat; molecular targeted therapy; oral squamous cell carcinoma.
Copyright © 2022 Altamura and Borzacchiello.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Monoclonal antibody cetuximab impairs matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9, epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cell migration in feline oral squamous cell carcinoma in vitro.Vet Comp Oncol. 2024 Mar;22(1):149-155. doi: 10.1111/vco.12943. Epub 2023 Nov 29. Vet Comp Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38030131
-
The Small Molecule BIBR1532 Exerts Potential Anti-cancer Activities in Preclinical Models of Feline Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Through Inhibition of Telomerase Activity and Down-Regulation of TERT.Front Vet Sci. 2021 Jan 20;7:620776. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2020.620776. eCollection 2020. Front Vet Sci. 2021. PMID: 33553285 Free PMC article.
-
p16, pRb, and p53 in Feline Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Vet Sci. 2016 Aug 18;3(3):18. doi: 10.3390/vetsci3030018. Vet Sci. 2016. PMID: 29056726 Free PMC article.
-
Cetuximab: an epidermal growth factor receptor chemeric human-murine monoclonal antibody.Drugs Today (Barc). 2005 Feb;41(2):107-27. doi: 10.1358/dot.2005.41.2.882662. Drugs Today (Barc). 2005. PMID: 15821783 Review.
-
The role of cetuximab in the treatment of squamous cell cancer of the head and neck.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2005 Aug;5(8):1085-93. doi: 10.1517/14712598.5.8.1085. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2005. PMID: 16050785 Review.
Cited by
-
Feline oral squamous cell carcinoma and Felis catus papillomavirus: is it time to walk the path of human oncology?Front Vet Sci. 2023 May 17;10:1148673. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1148673. eCollection 2023. Front Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 37266382 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
A Scoping Review on Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Cats: Current Evidence and Future Directions.Animals (Basel). 2023 Sep 29;13(19):3059. doi: 10.3390/ani13193059. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37835664 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A meta-validated immune infiltration-related gene model predicts prognosis and immunotherapy sensitivity in HNSCC.BMC Cancer. 2023 Jan 13;23(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-10532-y. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36639648 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating Cox-2 and EGFR as Biomarkers in Canine Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Implications for Diagnosis and Therapy.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Jan 4;46(1):485-497. doi: 10.3390/cimb46010031. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38248333 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

