Exosomes as a Cell-free Therapy for Myocardial Injury Following Acute Myocardial Infarction or Ischemic Reperfusion
- PMID: 36465167
- PMCID: PMC9662265
- DOI: 10.14336/AD.2022.0416
Exosomes as a Cell-free Therapy for Myocardial Injury Following Acute Myocardial Infarction or Ischemic Reperfusion
Abstract
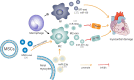
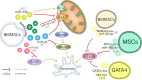
Exosomes, which contain miRNA, have been receiving growing attention in cardiovascular therapy because of their role in mediating cell-cell communication, autophagy, apoptosis, inflammation, and angiogenesis. Several studies have suggested that miRNA derived from exosomes can be used to detect myocardial infarctions (MI) in patients. Basic research also suggests that exosomes could serve as a potential therapeutic target for treating acute myocardial infarction. Ischemia/reperfusion (IR) injury is associated with adverse cardiac events after acute MI. We aim to review the potential benefits and mechanisms of exosomes in treating MI and IR injury.
Keywords: acute myocardial infarction; cell-free therapy; exosome; ischemic reperfusion.
copyright: © 2022 An et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare no competing interests
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exosome Derived from Coronary Serum of Patients with Myocardial Infarction Promotes Angiogenesis Through the miRNA-143/IGF-IR Pathway.Int J Nanomedicine. 2020 Apr 21;15:2647-2658. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S242908. eCollection 2020. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020. PMID: 32368046 Free PMC article.
-
Cell Death and Exosomes Regulation After Myocardial Infarction and Ischemia-Reperfusion.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jun 9;9:673677. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.673677. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34179002 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomes derived from SDF1-overexpressing mesenchymal stem cells inhibit ischemic myocardial cell apoptosis and promote cardiac endothelial microvascular regeneration in mice with myocardial infarction.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Aug;234(8):13878-13893. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28070. Epub 2019 Feb 5. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30720220
-
Plasma Exosomes at the Late Phase of Remote Ischemic Pre-conditioning Attenuate Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Through Transferring miR-126a-3p.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Nov 30;8:736226. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.736226. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34917657 Free PMC article.
-
Role of miRNA-1 and miRNA-21 in Acute Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury and Their Potential as Therapeutic Strategy.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 28;23(3):1512. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031512. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163436 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of left ventricular dysfunction by three-dimensional speckle-tracking echocardiography and bioinformatics analysis of circulating exosomal miRNA in obese patients.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2023 Sep 11;23(1):450. doi: 10.1186/s12872-023-03502-6. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2023. PMID: 37697228 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic application of adipose-derived stromal vascular fraction in myocardial infarction.iScience. 2024 Apr 18;27(5):109791. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109791. eCollection 2024 May 17. iScience. 2024. PMID: 38736548 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomes-mediated drug delivery for the treatment of myocardial injury.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2023 Dec 2;86(1):292-299. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000001473. eCollection 2024 Jan. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2023. PMID: 38222684 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal mir-21-5p inhibits YAP1 expression and improves outcomes in myocardial infarction.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024 Oct 10;24(1):547. doi: 10.1186/s12872-024-04197-z. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024. PMID: 39385107 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil N1 polarization induced by cardiomyocyte-derived extracellular vesicle miR-9-5p aggravates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Oct 16;22(1):632. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02902-w. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 39415256 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Simons M, Raposo G (2009). Exosomes--vesicular carriers for intercellular communication. Curr Opin Cell Biol, 21:575-581. - PubMed
-
- Mathivanan S, Ji H, Simpson RJ (2010). Exosomes: extracellular organelles important in intercellular communication. J Proteomics, 73:1907-1920. - PubMed
-
- Gross JC, Chaudhary V, Bartscherer K, Boutros M (2012). Active Wnt proteins are secreted on exosomes. Nat Cell Biol, 14:1036-1045. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
