Twisting development, the birth of a potential new gene
- PMID: 36465114
- PMCID: PMC9713375
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.105627
Twisting development, the birth of a potential new gene
Abstract
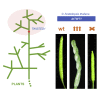
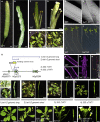
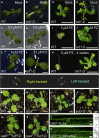
Evolution has long been considered to be a conservative process in which new genes arise from pre-existing genes through gene duplication, domain shuffling, horizontal transfer, overprinting, retrotransposition, etc. However, this view is changing as new genes originating from non-genic sequences are discovered in different organisms. Still, rather limited functional information is available. Here, we have identified TWISTED1 (TWT1), a possible de novo-originated protein-coding gene that modifies microtubule arrangement and causes helicoidal growth in Arabidopsis thaliana when its expression is increased. Interestingly, even though TWT1 is a likely recent gene, the lack of TWT1 function affects A. thaliana development. TWT1 seems to have originated from a non-genic sequence. If so, it would be one of the few examples to date of how during evolution de novo genes are integrated into developmental cellular and organismal processes.
Keywords: Evolutionary biology; Molecular biology; Plant development.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Proto-genes and de novo gene birth.Nature. 2012 Jul 19;487(7407):370-4. doi: 10.1038/nature11184. Nature. 2012. PMID: 22722833 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary origins of Brassicaceae specific genes in Arabidopsis thaliana.BMC Evol Biol. 2011 Feb 18;11:47. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-11-47. BMC Evol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21332978 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of microRNA genes in Oryza sativa and Arabidopsis thaliana: an update of the inverted duplication model.PLoS One. 2011;6(12):e28073. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028073. Epub 2011 Dec 14. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22194805 Free PMC article.
-
The Origins and Functions of De Novo Genes: Against All Odds?J Mol Evol. 2022 Aug;90(3-4):244-257. doi: 10.1007/s00239-022-10055-3. Epub 2022 Apr 22. J Mol Evol. 2022. PMID: 35451603 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evolution of new functions de novo and from preexisting genes.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015 Jun 1;7(6):a017996. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a017996. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015. PMID: 26032716 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Four classic "de novo" genes all have plausible homologs and likely evolved from retro-duplicated or pseudogenic sequences.Mol Genet Genomics. 2024 Feb 5;299(1):6. doi: 10.1007/s00438-023-02090-6. Mol Genet Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38315248
-
High-throughput Selection of Human de novo-emerged sORFs with High Folding Potential.Genome Biol Evol. 2024 Apr 2;16(4):evae069. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evae069. Genome Biol Evol. 2024. PMID: 38597156 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ohno S. Springer-Verlag; 1970. Evolution by Gene Duplication.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

