Benchmarking challenging small variants with linked and long reads
- PMID: 36452119
- PMCID: PMC9706577
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xgen.2022.100128
Benchmarking challenging small variants with linked and long reads
Abstract
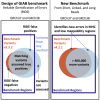
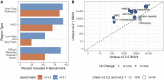
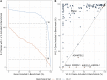
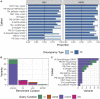
Genome in a Bottle benchmarks are widely used to help validate clinical sequencing pipelines and develop variant calling and sequencing methods. Here we use accurate linked and long reads to expand benchmarks in 7 samples to include difficult-to-map regions and segmental duplications that are challenging for short reads. These benchmarks add more than 300,000 SNVs and 50,000 insertions or deletions (indels) and include 16% more exonic variants, many in challenging, clinically relevant genes not covered previously, such as PMS2. For HG002, we include 92% of the autosomal GRCh38 assembly while excluding regions problematic for benchmarking small variants, such as copy number variants, that should not have been in the previous version, which included 85% of GRCh38. It identifies eight times more false negatives in a short read variant call set relative to our previous benchmark. We demonstrate that this benchmark reliably identifies false positives and false negatives across technologies, enabling ongoing methods development.
Conflict of interest statement
A.M.W. and W.J.R. are employees and shareholders of Pacific Biosciences. A.M.B. and I.T.F. were employees and shareholders of 10X Genomics. F.J.S. has received sponsored travel from Oxford Nanopore and Pacific Biosciences and a 2018 sequencing grant from Pacific Biosciences. A.S. and V.K. are employees of Seven Bridges. A.C. is an employee of Google Inc. and a former employee of DNAnexus. A.F. and C.-S.C. are employees of DNAnexus.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Curated variation benchmarks for challenging medically relevant autosomal genes.Nat Biotechnol. 2022 May;40(5):672-680. doi: 10.1038/s41587-021-01158-1. Epub 2022 Feb 7. Nat Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35132260 Free PMC article.
-
PrecisionFDA Truth Challenge V2: Calling variants from short and long reads in difficult-to-map regions.Cell Genom. 2022 May 11;2(5):100129. doi: 10.1016/j.xgen.2022.100129. Epub 2022 Apr 27. Cell Genom. 2022. PMID: 35720974 Free PMC article.
-
Benchmarking datasets for assembly-based variant calling using high-fidelity long reads.BMC Genomics. 2023 Mar 27;24(1):148. doi: 10.1186/s12864-023-09255-y. BMC Genomics. 2023. PMID: 36973656 Free PMC article.
-
A diploid assembly-based benchmark for variants in the major histocompatibility complex.Nat Commun. 2020 Sep 22;11(1):4794. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18564-9. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32963235 Free PMC article.
-
Haplotyping-Assisted Diploid Assembly and Variant Detection with Linked Reads.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2590:161-182. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2819-5_11. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36335499 Review.
Cited by
-
xAtlas: scalable small variant calling across heterogeneous next-generation sequencing experiments.Gigascience. 2022 Dec 28;12:giac125. doi: 10.1093/gigascience/giac125. Epub 2023 Jan 16. Gigascience. 2022. PMID: 36644891 Free PMC article.
-
Towards population-scale long-read sequencing.Nat Rev Genet. 2021 Sep;22(9):572-587. doi: 10.1038/s41576-021-00367-3. Epub 2021 May 28. Nat Rev Genet. 2021. PMID: 34050336 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A genome sequencing system for universal newborn screening, diagnosis, and precision medicine for severe genetic diseases.Am J Hum Genet. 2022 Sep 1;109(9):1605-1619. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2022.08.003. Epub 2022 Aug 24. Am J Hum Genet. 2022. PMID: 36007526 Free PMC article. Review.
-
WarpSTR: determining tandem repeat lengths using raw nanopore signals.Bioinformatics. 2023 Jun 1;39(6):btad388. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btad388. Bioinformatics. 2023. PMID: 37326967 Free PMC article.
-
Multiscale analysis of pangenomes enables improved representation of genomic diversity for repetitive and clinically relevant genes.Nat Methods. 2023 Aug;20(8):1213-1221. doi: 10.1038/s41592-023-01914-y. Epub 2023 Jun 26. Nat Methods. 2023. PMID: 37365340 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zook J.M., Chapman B., Wang J., Mittelman D., Hofmann O., Hide W., Salit M. Integrating human sequence data sets provides a resource of benchmark SNP and indel genotype calls. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014;32:246–251. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

