GSK3α phosphorylates dynamin-2 to promote GLUT4 endocytosis in muscle cells
- PMID: 36445308
- PMCID: PMC9712776
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.202102119
GSK3α phosphorylates dynamin-2 to promote GLUT4 endocytosis in muscle cells
Abstract
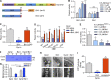
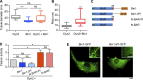
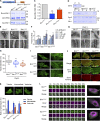
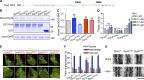
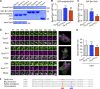
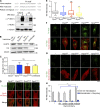
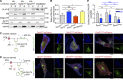
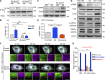
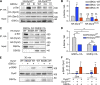
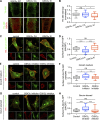
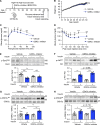
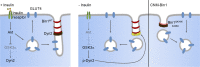
Insulin-stimulated translocation of glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4) to plasma membrane of skeletal muscle is critical for postprandial glucose uptake; however, whether the internalization of GLUT4 is also regulated by insulin signaling remains unclear. Here, we discover that the activity of dynamin-2 (Dyn2) in catalyzing GLUT4 endocytosis is negatively regulated by insulin signaling in muscle cells. Mechanistically, the fission activity of Dyn2 is inhibited by binding with the SH3 domain of Bin1. In the absence of insulin, GSK3α phosphorylates Dyn2 to relieve the inhibition of Bin1 and promotes endocytosis. Conversely, insulin signaling inactivates GSK3α and leads to attenuated GLUT4 internalization. Furthermore, the isoform-specific pharmacological inhibition of GSK3α significantly improves insulin sensitivity and glucose tolerance in diet-induced insulin-resistant mice. Together, we identify a new role of GSK3α in insulin-stimulated glucose disposal by regulating Dyn2-mediated GLUT4 endocytosis in muscle cells. These results highlight the isoform-specific function of GSK3α on membrane trafficking and its potential as a therapeutic target for metabolic disorders.
© 2022 Laiman et al.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Perturbation of dynamin II with an amphiphysin SH3 domain increases GLUT4 glucose transporters at the plasma membrane in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Dynamin II participates in GLUT4 endocytosis.J Biol Chem. 1998 Apr 3;273(14):8169-76. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.14.8169. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9525921
-
Ready, set, internalize: mechanisms and regulation of GLUT4 endocytosis.Biosci Rep. 2009 Feb;29(1):1-11. doi: 10.1042/BSR20080105. Biosci Rep. 2009. PMID: 19143591 Review.
-
The F-BAR protein CIP4 promotes GLUT4 endocytosis through bidirectional interactions with N-WASp and Dynamin-2.J Cell Sci. 2009 Jul 1;122(Pt 13):2283-91. doi: 10.1242/jcs.041343. Epub 2009 Jun 9. J Cell Sci. 2009. PMID: 19509061 Free PMC article.
-
Intracellular organization of insulin signaling and GLUT4 translocation.Recent Prog Horm Res. 2001;56:175-93. doi: 10.1210/rp.56.1.175. Recent Prog Horm Res. 2001. PMID: 11237212 Review.
-
Dimethyl sulfoxide enhances GLUT4 translocation through a reduction in GLUT4 endocytosis in insulin-stimulated 3T3-L1 adipocytes.Biochimie. 2011 Apr;93(4):697-709. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2010.12.013. Epub 2010 Dec 30. Biochimie. 2011. PMID: 21195125
Cited by
-
Dynamics of membrane tubulation coupled with fission by a two-component module.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 May 14;121(20):e2402180121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2402180121. Epub 2024 May 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38717859 Free PMC article.
-
Uncovering the BIN1-SH3 interactome underpinning centronuclear myopathy.Elife. 2024 Jul 12;13:RP95397. doi: 10.7554/eLife.95397. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38995680 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin signalling and GLUT4 trafficking in insulin resistance.Biochem Soc Trans. 2023 Jun 28;51(3):1057-1069. doi: 10.1042/BST20221066. Biochem Soc Trans. 2023. PMID: 37248992 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahmad, F., Lal H., Zhou J., Vagnozzi R.J., Yu J.E., Shang X., Woodgett J.R., Gao E., and Force T.. 2014. Cardiomyocyte-specific deletion of Gsk3α mitigates post-myocardial infarction remodeling, contractile dysfunction, and heart failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 64:696–706. 10.1016/j.jacc.2014.04.068 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Batista, T.M., Jayavelu A.K., Wewer Albrechtsen N.J., Iovino S., Lebastchi J., Pan H., Dreyfuss J.M., Krook A., Zierath J.R., Mann M., and Kahn C.R.. 2020. A cell-autonomous signature of dysregulated protein phosphorylation underlies muscle insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes. Cell Metab. 32:844–859.e5. 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.08.007 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

