Comprehensive analysis of ID genes reveals the clinical and prognostic value of ID3 expression in acute myeloid leukemia using bioinformatics identification and experimental validation
- PMID: 36443709
- PMCID: PMC9707109
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-022-10352-6
Comprehensive analysis of ID genes reveals the clinical and prognostic value of ID3 expression in acute myeloid leukemia using bioinformatics identification and experimental validation
Abstract
Background: Dysregulation of inhibitor of differentiation/DNA binding (ID) genes is linked to cancer growth, angiogenesis, invasiveness, metastasis and patient survival. Nevertheless, few investigations have systematically determined the expression and prognostic value of ID genes in acute myeloid leukemia (AML).
Methods: The expression and clinical prognostic value of ID genes in AML were first identified by public databases and further validated by our research cohort.
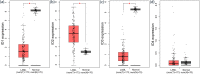
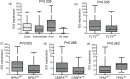
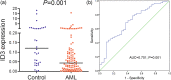
Results: Using public data, the expression of ID1/ID3 was markedly downregulated in AML, and the expression of ID2 was greatly upregulated in AML, whereas ID4 showed no significant difference. Among the ID genes, only ID3 expression may be the most valuable prognostic biomarker in both total AML and cytogenetically normal AML (CN-AML) and especially in CN-AML. Clinically, reduced ID3 expression was greatly associated with higher white blood cell counts, peripheral blood/bone marrow blasts, normal karyotypes and intermediate cytogenetic risk. In addition, low ID3 expression was markedly related to FLT3 and NPM1 mutations as well as wild-type TP53. Despite these associations, multivariate Cox regression analysis revealed that ID3 expression was an independent risk factor affecting overall survival (OS) and disease free survival (DFS) in CN-AML patients. Biologically, a total of 839 mRNAs/lncRNAs and 72 microRNAs were found to be associated with ID3 expression in AML. Importantly, the expression of ID3 with discriminative value in AML was further confirmed in our research cohort.
Conclusion: The bioinformatics analysis and experimental verification demonstrate that low ID3 expression independently affects OS and DFS in patients with CN-AML, which might be seen as a potential prognostic indicator in CN-AML.
Keywords: AML; Expression; ID; ID3; Prognosis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prognostic implications of NPM1 mutations and FLT3 internal tandem duplications in Egyptian patients with cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia.Hematology. 2014 Jan;19(1):22-30. doi: 10.1179/1607845413Y.0000000085. Epub 2013 Nov 25. Hematology. 2014. PMID: 23540998
-
Clinical significance of FLT3-ITD/CEBPA mutations and minimal residual disease in cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2021 Sep;147(9):2659-2670. doi: 10.1007/s00432-021-03530-9. Epub 2021 Feb 7. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33550446
-
Favorable prognostic impact of NPM1 mutations in older patients with cytogenetically normal de novo acute myeloid leukemia and associated gene- and microRNA-expression signatures: a Cancer and Leukemia Group B study.J Clin Oncol. 2010 Feb 1;28(4):596-604. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.25.1496. Epub 2009 Dec 21. J Clin Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20026798 Free PMC article.
-
Hormonal regulation and differential actions of the helix-loop-helix transcriptional inhibitors of differentiation (Id1, Id2, Id3, and Id4) in Sertoli cells.Endocrinology. 2001 May;142(5):1727-36. doi: 10.1210/endo.142.5.8134. Endocrinology. 2001. PMID: 11316735
-
Prognostic significance of FLT3 internal tandem duplication, nucleophosmin 1, and CEBPA gene mutations for acute myeloid leukemia patients with normal karyotype and younger than 60 years: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Ann Hematol. 2014 Aug;93(8):1279-86. doi: 10.1007/s00277-014-2072-6. Epub 2014 May 7. Ann Hematol. 2014. PMID: 24801015 Review.
References
-
- Döhner H, Estey E, Grimwade D, Amadori S, Appelbaum FR, Büchner T, Dombret H, Ebert BL, Fenaux P, Larson RA, Levine RL, Lo-Coco F, Naoe T, Niederwieser D, Ossenkoppele GJ, Sanz M, Sierra J, Tallman MS, Tien HF, Wei AH, Löwenberg B, Bloomfield CD. Diagnosis and management of AML in adults: 2017 ELN recommendations from an international expert panel. Blood. 2017;129(4):424–47. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-08-733196. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

