Association between physical activity and serum liver aminotransferases in Southwestern Iran: A Cross-sectional study
- PMID: 36438076
- PMCID: PMC9693751
- DOI: 10.4103/jrms.jrms_835_21
Association between physical activity and serum liver aminotransferases in Southwestern Iran: A Cross-sectional study
Abstract
Background: The main aim of the present study is to investigate the independent association objectively measured level of physical activity (PA) and serum concentration of liver aminotransferases (alanine aminotransferase [ALT] and aspartate aminotransferase [AST]) among seemingly healthy individuals.
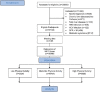
Materials and methods: The current secondary study was conducted in the framework of Khuzestan Comprehensive Health Study, a large population-based multicentric cross-sectional study, conducted between 2016 and 2019 on 18,966 individuals living in Khuzestan province, southwestern Iran. International PA Questionnaire was used for evaluating PA levels, and participants were divided into three groups: low, moderate, and high PA, and ALT and AST were compared between these groups.
Results: The mean ± standard deviation age of participants was 38.65 ± 11.40 years. The majority of participants were female (71%). The mean concentration of ALT in total sample was 18.22 ± 13.06 (male: 23.65 ± 16.26 and female: 15.57 ± 10.06), while the mean concentration of ALT in total sample was 19.61 ± 8.40 (male: 22.44 ± 10.03 and female: 18.23 ± 7.08). A statistically significant inverse correlation was found between AST (r = -0.08, P = 0.02) and ALT (r = -0.038, P < 0.001) with total PA score. The mean concentration of ALT was 19.96 ± 13.63 in people with low PA, 17.62 ± 12.31 with moderate PA, and 18.12 ± 13.47 with high PA (P < 0.001). The mean concentration of AST in total sample was 20.37 ± 8.85 in people with low PA, 19.21 ± 8.83 with moderate PA, and 19.75 ± 8.85 with high PA (P < 0.001). The difference between people in different levels of PA in terms of mean concentration of AST was remained significant (P = 0.003); however, the difference for ALT was not remained significant after adjusting potential confounders.
Conclusion: The current study based on large sample showed that PA had a statistically negative association with the concentration of liver aminotransferases in the seemingly healthy individuals; however, the observed associations were weak. People in the lowest levels of PA had the highest levels of ALT and AST.
Keywords: Alanine aminotransferase; aspartate aminotransferase; liver aminotransferase; physical activity.
Copyright: © 2022 Journal of Research in Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Body Adiposity, But Not Elements of Objectively Measured Sedentary Behavior or Physical Activity, Is Associated With Circulating Liver Enzymes in Adults With Overweight and Obesity.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Apr 20;12:655756. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.655756. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 33959099 Free PMC article.
-
Serum gamma-glutamyltransferase, alanine aminotransferase, and aspartate aminotransferase activity in Iranian healthy blood donor men.World J Gastroenterol. 2007 Feb 14;13(6):889-94. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i6.889. World J Gastroenterol. 2007. PMID: 17352018 Free PMC article.
-
Decreased serum aminotransferase activity in patients with chronic renal failure: impact on the detection of viral hepatitis.Am J Kidney Dis. 2001 Nov;38(5):1009-15. doi: 10.1053/ajkd.2001.28590. Am J Kidney Dis. 2001. PMID: 11684554
-
Physical activity, sedentary time, and liver enzymes in adolescents: the HELENA study.Pediatr Res. 2014 Jun;75(6):798-802. doi: 10.1038/pr.2014.26. Epub 2014 Mar 6. Pediatr Res. 2014. PMID: 24603293
-
AST to ALT ratio and arterial stiffness in non-fatty liver Japanese population:a secondary analysis based on a cross-sectional study.Lipids Health Dis. 2018 Dec 3;17(1):275. doi: 10.1186/s12944-018-0920-4. Lipids Health Dis. 2018. PMID: 30509277 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Physiological changes in captive elephants in Northern Thailand as a result of the COVID-19 tourism ban - muscle, liver, metabolic function, and body condition.Front Vet Sci. 2023 Dec 21;10:1303537. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1303537. eCollection 2023. Front Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 38179326 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Verslype C. Evaluation of abnormal liver-enzyme results in asymptomatic patients. Acta Clin Belg. 2004;59:285–9. - PubMed
-
- Mathiesen UL, Franzén LE, Frydén A, Foberg U, Bodemar G. The clinical significance of slightly to moderately increased liver transaminase values in asymptomatic patients. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1999;34:85–91. - PubMed
-
- Berzigotti A, Saran U, Dufour JF. Physical activity and liver diseases. Hepatology. 2016;63:1026–40. - PubMed
-
- Dumith SC, Hallal PC, Reis RS, Kohl HW., 3rd Worldwide prevalence of physical inactivity and its association with human development index in 76 countries. Prev Med. 2011;53:24–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources