Extracellular signals regulate the biogenesis of extracellular vesicles
- PMID: 36435789
- PMCID: PMC9701380
- DOI: 10.1186/s40659-022-00405-2
Extracellular signals regulate the biogenesis of extracellular vesicles
Abstract
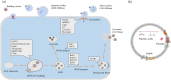
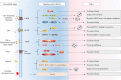
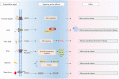
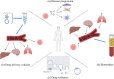
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are naturally released membrane vesicles that act as carriers of proteins and RNAs for intercellular communication. With various biomolecules and specific ligands, EV has represented a novel form of information transfer, which possesses extremely outstanding efficiency and specificity compared to the classical signal transduction. In addition, EV has extended the concept of signal transduction to intercellular aspect by working as the collection of extracellular information. Therefore, the functions of EVs have been extensively characterized and EVs exhibit an exciting prospect for clinical applications. However, the biogenesis of EVs and, in particular, the regulation of this process by extracellular signals, which are essential to conduct further studies and support optimal utility, remain unclear. Here, we review the current understanding of the biogenesis of EVs, focus on the regulation of this process by extracellular signals and discuss their therapeutic value.
Keywords: Exosome; Extracellular signal; Extracellular vesicle; Information transfer; Microvesicle; Signal transduction.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Focus on Extracellular Vesicles: Physiological Role and Signalling Properties of Extracellular Membrane Vesicles.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Feb 6;17(2):171. doi: 10.3390/ijms17020171. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 26861302 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicles and Their Emerging Roles as Cellular Messengers in Endocrinology: An Endocrine Society Scientific Statement.Endocr Rev. 2022 May 12;43(3):441-468. doi: 10.1210/endrev/bnac009. Endocr Rev. 2022. PMID: 35552682 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular vesicle interplay in cardiovascular pathophysiology.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2021 May 1;320(5):H1749-H1761. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00925.2020. Epub 2021 Mar 5. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33666501 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review of the regulatory mechanisms of extracellular vesicles-mediated intercellular communication.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Apr 13;21(1):77. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01103-6. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 37055761 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Focus on Extracellular Vesicles: Introducing the Next Small Big Thing.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Feb 6;17(2):170. doi: 10.3390/ijms17020170. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 26861301 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Research Advances on Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Promoting the Reconstruction of Alveolar Bone through RANKL/RANK/OPG Pathway.J Funct Biomater. 2023 Mar 30;14(4):193. doi: 10.3390/jfb14040193. J Funct Biomater. 2023. PMID: 37103283 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular vesicles as modulators of glioblastoma progression and tumor microenvironment.Pathol Oncol Res. 2024 Feb 6;30:1611549. doi: 10.3389/pore.2024.1611549. eCollection 2024. Pathol Oncol Res. 2024. PMID: 38379858 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unraveling the Multifaceted Roles of Extracellular Vesicles: Insights into Biology, Pharmacology, and Pharmaceutical Applications for Drug Delivery.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 29;25(1):485. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010485. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38203656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interstitial Fluid Shear Stress Induces the Synthetic Phenotype Switching of VSMCs to Release Pro-calcified Extracellular Vesicles via EGFR-MAPK-KLF5 Pathway.Int J Biol Sci. 2024 Apr 29;20(7):2727-2747. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.90725. eCollection 2024. Int J Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38725857 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Vesicles and Their Renin-Angiotensin Cargo as a Link between Metabolic Syndrome and Parkinson's Disease.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Nov 26;12(12):2045. doi: 10.3390/antiox12122045. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38136165 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Harding C, Heuser J, Stahl P. Endocytosis and intracellular processing of transferrin and colloidal gold-transferrin in rat reticulocytes: demonstration of a pathway for receptor shedding. Eur J Cell Biol. 1984;35(2):256–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

