Porphyrin Polymers Bearing N, N'-Ethylene Crosslinkers as Photosensitizers against Bacteria
- PMID: 36433062
- PMCID: PMC9696963
- DOI: 10.3390/polym14224936
Porphyrin Polymers Bearing N, N'-Ethylene Crosslinkers as Photosensitizers against Bacteria
Abstract
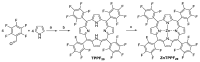
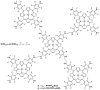
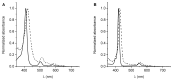
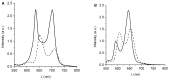
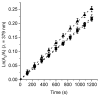
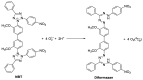
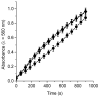
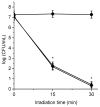
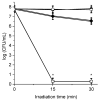
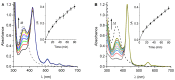
The appearance of microbes resistant to antibiotics requires the development of alternative therapies for the treatment of infectious diseases. In this work two polymers, PTPPF16-EDA and PZnTPPF16-EDA, were synthesized by the nucleophilic aromatic substitution of 5,10,15,20-tetrakis(pentafluorophenyl)porphyrin and its Zn(II) complex with ethylenediamine, respectively. In these structures, the tetrapyrrolic macrocycles were N,N'-ethylene crosslinked, which gives them greater mobility. The absorption spectra of the polymers showed a bathochromic shift of the Soret band of ~10 nm with respect to the monomers. This effect was also found in the red fluorescence emission peaks. Furthermore, both polymeric materials produced singlet molecular oxygen with high quantum yields. In addition, they were capable of generating superoxide anion radicals. Photodynamic inactivation sensitized by these polymers was tested in Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli bacteria. A decrease in cell viability greater than 7 log (99.9999%) was observed in S. aureus incubated with 0.5 μM photosensitizer upon 30 min of irradiation. Under these conditions, a low inactivation of E. coli (0.5 log) was found. However, when the cells were treated with KI, the elimination of the Gram-negative bacteria was achieved. Therefore, these polymeric structures are interesting antimicrobial photosensitizing materials for the inactivation of pathogens.
Keywords: antimicrobial; photodynamic inactivation; polymer; porphyrin; singlet oxygen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
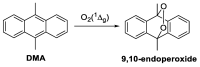
Similar articles
-
Porphyrins containing basic aliphatic amino groups as potential broad-spectrum antimicrobial agents.Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2018 Dec;24:220-227. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2018.09.017. Epub 2018 Sep 29. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2018. PMID: 30278279
-
Antimicrobial Photosensitizing Material Based on Conjugated Zn(II) Porphyrins.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Jan 12;11(1):91. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11010091. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35052968 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial Photodynamic Polymeric Films Bearing Biscarbazol Triphenylamine End-Capped Dendrimeric Zn(II) Porphyrin.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019 Aug 7;11(31):27574-27587. doi: 10.1021/acsami.9b09119. Epub 2019 Jul 29. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019. PMID: 31310503
-
Critical Overview of the Use of Ru(II) Polypyridyl Complexes as Photosensitizers in One-Photon and Two-Photon Photodynamic Therapy.Acc Chem Res. 2017 Nov 21;50(11):2727-2736. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.7b00180. Epub 2017 Oct 23. Acc Chem Res. 2017. PMID: 29058879 Review.
-
Synthesis of Photosensitizers Based on Tetrapyrrolic Macrocycles for Combination with Antibiotics: Dual Inactivation of Bacteria.Chempluschem. 2022 Nov;87(11):e202200228. doi: 10.1002/cplu.202200228. Chempluschem. 2022. PMID: 36351700 Review.
Cited by
-
An ambipolar PEDOT-perfluorinated porphyrin electropolymer: application as an active material in energy storage systems.RSC Adv. 2024 May 16;14(23):15929-15941. doi: 10.1039/d4ra00945b. eCollection 2024 May 15. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 38756855 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ioannou P., Karakonstantis S., Schouten J., Kostyanev T., Charani E., Vlahovic-Palcevski V., Kofteridis D.P. Indications for medical antibiotic prophylaxis and potential targets for antimicrobial stewardship intervention: A narrative review. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021;28:362–370. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2021.10.001. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

