Application of Peptides in Construction of Nonviral Vectors for Gene Delivery
- PMID: 36432361
- PMCID: PMC9693978
- DOI: 10.3390/nano12224076
Application of Peptides in Construction of Nonviral Vectors for Gene Delivery
Abstract
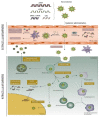
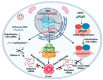
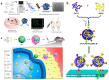
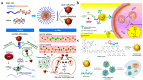
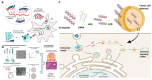
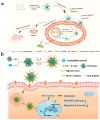
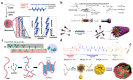
Gene therapy, which aims to cure diseases by knocking out, editing, correcting or compensating abnormal genes, provides new strategies for the treatment of tumors, genetic diseases and other diseases that are closely related to human gene abnormalities. In order to deliver genes efficiently to abnormal sites in vivo to achieve therapeutic effects, a variety of gene vectors have been designed. Among them, peptide-based vectors show superior advantages because of their ease of design, perfect biocompatibility and safety. Rationally designed peptides can carry nucleic acids into cells to perform therapeutic effects by overcoming a series of biological barriers including cellular uptake, endosomal escape, nuclear entrance and so on. Moreover, peptides can also be incorporated into other delivery systems as functional segments. In this review, we referred to the biological barriers for gene delivery in vivo and discussed several kinds of peptide-based nonviral gene vectors developed for overcoming these barriers. These vectors can deliver different types of genetic materials into targeted cells/tissues individually or in combination by having specific structure-function relationships. Based on the general review of peptide-based gene delivery systems, the current challenges and future perspectives in development of peptidic nonviral vectors for clinical applications were also put forward, with the aim of providing guidance towards the rational design and development of such systems.
Keywords: gene delivery; gene therapy; nonviral vector; peptide; self-assembly.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Designed Peptide Assemblies for Efficient Gene Delivery.Langmuir. 2022 Nov 15;38(45):13627-13634. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.2c02197. Epub 2022 Nov 1. Langmuir. 2022. PMID: 36318179 Review.
-
Recent advances in nonviral vectors for gene delivery.Acc Chem Res. 2012 Jul 17;45(7):971-9. doi: 10.1021/ar200151m. Epub 2011 Aug 26. Acc Chem Res. 2012. PMID: 21870813 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid-based Non-viral Vector: Promising Approach for Gene Delivery.Curr Pharm Des. 2024 Sep 24. doi: 10.2174/0113816128324084240828084904. Online ahead of print. Curr Pharm Des. 2024. PMID: 39318208
-
Peptide vectors for gene delivery: from single peptides to multifunctional peptide nanocarriers.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2014 Jul;9(14):2217-32. doi: 10.2217/nnm.14.90. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2014. PMID: 25405798 Review.
-
Recent advances in characterization of nonviral vectors for delivery of nucleic acids: impact on their biological performance.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2015 Jan;12(1):27-39. doi: 10.1517/17425247.2014.945421. Epub 2014 Aug 21. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2015. PMID: 25141765 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of Functional Nanomaterials for Applications in Chemical Engineering.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023 Feb 3;13(3):609. doi: 10.3390/nano13030609. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36770571 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhu Y., Shen R., Vuong I., Reynolds R.A., Shears M.J., Yao Z.-C., Hu Y., Cho W.J., Kong J., Reddy S.K., et al. Multistep screening of DNA/lipid nanoparticles and co-delivery with siRNA to enhance and prolong gene expression. Nat. Commun. 2022;13:4282. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-31993-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

