The C30-Modulation of Betulinic Acid Using 1,2,4-Triazole: A Promising Strategy for Increasing Its Antimelanoma Cytotoxic Potential
- PMID: 36431906
- PMCID: PMC9697306
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27227807
The C30-Modulation of Betulinic Acid Using 1,2,4-Triazole: A Promising Strategy for Increasing Its Antimelanoma Cytotoxic Potential
Abstract
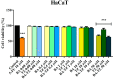
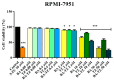
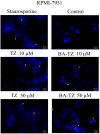
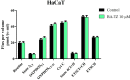
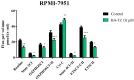
Cancer, in all its types and manifestations, remains one of the most frequent causes of death worldwide; an important number of anticancer drugs have been developed from plants, fungi and animals, starting with natural compounds that were later derivatized in order to achieve an optimized pharmacokinetic/pharmacological profile. Betulinic acid is a pentacyclic triterpenic compound that was identified as an anticancer agent whose main advantage consists in its selective activity, which ensures the almost total lack of cytotoxic side effects. Conjugates of betulinic acid with substituted triazoles, scaffolds with significant pharmacological properties, were synthesized and tested as anticancer agents in order to achieve new therapeutic alternatives. The current paper aims to obtain a C30-1,2,4-triazole derivative of betulinic acid simultaneously acetylated at C3 whose biological activity was tested against RPMI melanoma cells. The compound revealed significant cytotoxic effects at the tested concentrations (2, 10 and 50 μΜ) by significantly decreasing the cell viability to 88.3%, 54.7% and 24.5%, respectively, as compared to the control. The compound's testing in normal HaCaT cells showed a lack of toxicity, which indicates its selective dose-dependent anticancer activity. The investigation of its underlying molecular mechanism revealed an apoptotic effect induced at the mitochondrial level, which was validated through high-resolution respirometry studies.
Keywords: apoptosis; betulinic acid; cell viability; high-resolution respirometry; triazole; triterpenes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A novel triazole derivative of betulinic acid induces extrinsic and intrinsic apoptosis in human leukemia HL-60 cells.Eur J Med Chem. 2016 Jan 27;108:104-116. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2015.11.018. Epub 2015 Nov 19. Eur J Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 26629862
-
Synthesis and cytotoxicity of triterpenoids derived from betulin and betulinic acid via click chemistry.J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2015;17(2):159-69. doi: 10.1080/10286020.2014.979164. Epub 2014 Nov 7. J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2015. PMID: 25379995
-
Novel Triterpenic Acid-Benzotriazole Esters Act as Pro-Apoptotic Antimelanoma Agents.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 1;23(17):9992. doi: 10.3390/ijms23179992. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36077389 Free PMC article.
-
Betulinic acid: a promising anticancer candidate.IDrugs. 2004 Apr;7(4):359-73. IDrugs. 2004. PMID: 15057642 Review.
-
Betulinic acid: A natural promising anticancer drug, current situation, and future perspectives.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2022 Dec;36(12):e23206. doi: 10.1002/jbt.23206. Epub 2022 Sep 19. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 36124371 Review.
Cited by
-
Enhanced Cytotoxicity and Antimelanoma Activity of Novel Semisynthetic Derivatives of Betulinic Acid with Indole Conjugation.Plants (Basel). 2023 Dec 21;13(1):36. doi: 10.3390/plants13010036. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38202344 Free PMC article.
-
Probing N-substituted 4-(5-mercapto-4-ethyl-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)-N-phenylpiperdine-1-carboxamides as potent 15-LOX inhibitors supported with ADME, DFT calculations and molecular docking studies.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 29;10(17):e35278. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35278. eCollection 2024 Sep 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39281606 Free PMC article.
-
Drug Delivery Systems of Betulin and Its Derivatives: An Overview.Biomedicines. 2024 May 24;12(6):1168. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12061168. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38927375 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progress in Antimelanoma Research of Natural Triterpenoids and Their Derivatives: Mechanisms of Action, Bioavailability Enhancement and Structure Modifications.Molecules. 2023 Nov 24;28(23):7763. doi: 10.3390/molecules28237763. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 38067491 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pisha E., Chai H., Lee I.-S., Chagwedera T.E., Farnsworth N.R., Cordell G.A., Beecher C.W.W., Fong H.H.S., Kinghorn A.D., Brown D.M., et al. Discovery of betulinic acid as a selective inhibitor of human melanoma that functions by induction of apoptosis. Nat. Med. 1995;1:1046–1051. doi: 10.1038/nm1095-1046. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

