TGF-β/Smad Signalling Activation by HTRA1 Regulates the Function of Human Lens Epithelial Cells and Its Mechanism in Posterior Subcapsular Congenital Cataract
- PMID: 36430917
- PMCID: PMC9692351
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms232214431
TGF-β/Smad Signalling Activation by HTRA1 Regulates the Function of Human Lens Epithelial Cells and Its Mechanism in Posterior Subcapsular Congenital Cataract
Abstract
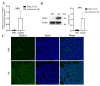
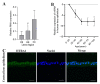
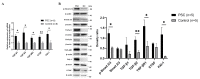
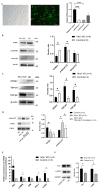
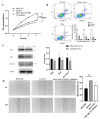
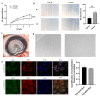
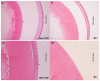
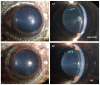
Congenital cataract is the leading cause of blindness among children worldwide. Patients with posterior subcapsular congenital cataract (PSC) in the central visual axis can result in worsening vision and stimulus deprivation amblyopia. However, the pathogenesis of PSC remains unclear. This study aims to explore the functional regulation and mechanism of HTRA1 in human lens epithelial cells (HLECs). HTRA1 was significantly downregulated in the lens capsules of children with PSC compared to normal controls. HTRA1 is a suppression factor of transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) signalling pathway, which plays a key role in cataract formation. The results showed that the TGF-β/Smad signalling pathway was activated in the lens tissue of PSC. The effect of HTRA1 on cell proliferation, migration and apoptosis was measured in HLECs. In primary HLECs, the downregulation of HTRA1 can promote the proliferation and migration of HLECs by activating the TGF-β/Smad signalling pathway and can significantly upregulate the TGF-β/Smad downstream target genes FN1 and α-SMA. HTRA1 was also knocked out in the eyes of C57BL/6J mice via adeno-associated virus-mediated RNA interference. The results showed that HTRA1 knockout can significantly upregulate p-Smad2/3 and activate the TGF-β/Smad signalling pathway, resulting in abnormal proliferation and irregular arrangement of lens epithelial cells and leading to the occurrence of subcapsular cataract. To conclude, HTRA1 was significantly downregulated in children with PSC, and the downregulation of HTRA1 enhanced the proliferation and migration of HLECs by activating the TGF-β/Smad signalling pathway, which led to the occurrence of PSC.
Keywords: HTRA1; TGF-β; lens epithelial cells; posterior subcapsular congenital cataract.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Arginase-1 promotes lens epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in different models of anterior subcapsular cataract.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Sep 18;21(1):236. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01210-4. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 37723490 Free PMC article.
-
High-temperature Requirement Protein A1 Regulates Odontoblastic Differentiation of Dental Pulp Cells via the Transforming Growth Factor Beta 1/Smad Signaling Pathway.J Endod. 2018 May;44(5):765-772. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2018.02.003. Epub 2018 Mar 24. J Endod. 2018. PMID: 29580722
-
Metformin attenuates the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of lens epithelial cells through the AMPK/TGF-β/Smad2/3 signalling pathway.Exp Eye Res. 2021 Nov;212:108763. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2021.108763. Epub 2021 Sep 10. Exp Eye Res. 2021. PMID: 34517004
-
Transforming growth factor-beta-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in the lens: a model for cataract formation.Cells Tissues Organs. 2005;179(1-2):43-55. doi: 10.1159/000084508. Cells Tissues Organs. 2005. PMID: 15942192 Review.
-
Transforming growth factor-β signalling: role and consequences of Smad linker region phosphorylation.Cell Signal. 2013 Oct;25(10):2017-24. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.06.001. Epub 2013 Jun 11. Cell Signal. 2013. PMID: 23770288 Review.
Cited by
-
Swimming exercise reverses transcriptomic changes in aging mouse lens.BMC Med Genomics. 2024 Mar 4;17(1):67. doi: 10.1186/s12920-024-01839-1. BMC Med Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38439070 Free PMC article.
-
Application of transgenic mice to the molecular pathogenesis of cataract.Int J Ophthalmol. 2024 Oct 18;17(10):1929-1948. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2024.10.21. eCollection 2024. Int J Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 39430018 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

