Melatonin Attenuates Ischemic-like Cell Injury by Promoting Autophagosome Maturation via the Sirt1/FoxO1/Rab7 Axis in Hippocampal HT22 Cells and in Organotypic Cultures
- PMID: 36429130
- PMCID: PMC9688641
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11223701
Melatonin Attenuates Ischemic-like Cell Injury by Promoting Autophagosome Maturation via the Sirt1/FoxO1/Rab7 Axis in Hippocampal HT22 Cells and in Organotypic Cultures
Abstract
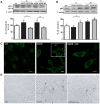
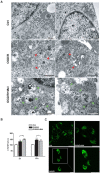
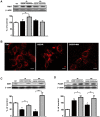
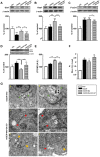
Dysfunctional autophagy is linked to neuronal damage in ischemia/reperfusion injury. The Ras-related protein 7 (Rab7), a member of the Rab family of small GTPases, appears crucial for the progression of the autophagic flux, and its activity is strictly interconnected with the histone deacetylase Silent information regulator 1 (Sirt1) and transcription factor Forkhead box class O1 (FoxO1). The present study assessed the neuroprotective role of melatonin in the modulation of the Sirt1/FoxO1/Rab7 axis in HT22 cells and organotypic hippocampal cultures exposed to oxygen-glucose deprivation followed by reoxygenation (OGD/R). The results showed that melatonin re-established physiological levels of autophagy and reduced propidium iodide-positive cells, speeding up autophagosome (AP) maturation and increasing lysosomal activity. Our study revealed that melatonin modulates autophagic pathways, increasing the expression of both Rab7 and FoxO1 and restoring the Sirt1 expression affected by OGD/R. In addition, the Sirt1 inhibitor EX-527 significantly reduced Rab7, Sirt1, and FoxO1 expression, as well as autolysosomes formation, and blocked the neuroprotective effect of melatonin. Overall, our findings provide, for the first time, new insights into the neuroprotective role of melatonin against ischemic injury through the activation of the Sirt1/FoxO1/Rab7 axis.
Keywords: Forkhead box class O1; Ras-related protein 7; autolysosome; autophagic flux; hippocampal slices; ischemia; silent information regulator 1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Acetylation of FOXO1 is involved in cadmium-induced rat kidney injury via mediating autophagosome-lysosome fusion blockade and autophagy inhibition.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2024 Nov 15;287:117253. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2024.117253. Epub 2024 Nov 12. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2024. PMID: 39536554
-
Naringenin attenuates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting oxidative stress and inflammatory response via the activation of SIRT1/FOXO1 signaling pathway in vitro.Acta Cir Bras. 2023 May 1;38:e380823. doi: 10.1590/acb380823. eCollection 2023. Acta Cir Bras. 2023. PMID: 37132753 Free PMC article.
-
[Silencing SIRT1 reduces 5-fluorouracil resistance of cholangiocarcinoma cells by inhibiting the FOXO1/Rab7 autophagy pathway].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2023 Mar 20;43(3):454-459. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2023.03.16. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2023. PMID: 37087591 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
SIRT1 is a regulator of autophagy: Implications for the progression and treatment of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion.Pharmacol Res. 2024 Jan;199:106957. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2023.106957. Epub 2023 Oct 10. Pharmacol Res. 2024. PMID: 37820856 Review.
-
New role of silent information regulator 1 in cerebral ischemia.Neurobiol Aging. 2013 Dec;34(12):2879-88. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2013.06.008. Epub 2013 Jul 12. Neurobiol Aging. 2013. PMID: 23855981 Review.
Cited by
-
Systematic review of melatonin in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury: critical role and therapeutic opportunities.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Feb 5;15:1356112. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1356112. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38375039 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Melatonin modulates the Notch1 signaling pathway and Sirt3 in the hippocampus of hypoxic-ischemic neonatal rats.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 23;14(1):25069. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-76307-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39443594 Free PMC article.
-
Melatonin: Facts, Extrapolations and Clinical Trials.Biomolecules. 2023 Jun 5;13(6):943. doi: 10.3390/biom13060943. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37371523 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ravikumar B., Sarkar S., Davies J.E., Futter M., Garcia-Arencibia M., Green-Thompson Z.W., Jimenez-Sanchez M., Korolchuk V., Lichtenberg M., Luo S., et al. Regulation of Mammalian Autophagy in Physiology and Pathophysiology. Physiol. Rev. 2010;90:1383–1435. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00030.2009. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

