α-Lipoic Acid Derivatives as Allosteric Modulators for Targeting AMPA-Type Glutamate Receptors' Gating Modules
- PMID: 36429036
- PMCID: PMC9688225
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11223608
α-Lipoic Acid Derivatives as Allosteric Modulators for Targeting AMPA-Type Glutamate Receptors' Gating Modules
Abstract
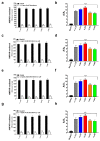
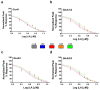
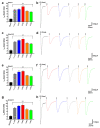
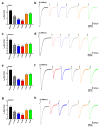
The ionotropic glutamate receptor subtype α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionic acid (AMPA) is responsible for most excitatory transmission in the brain. AMPA receptor function is altered in numerous neurological illnesses, making AMPA receptors appealing therapeutic targets for clinical intervention. Alpha-Lipoic acid (α-LA) is a naturally occurring compound, which functions as a co-factor in metabolism and energy production. α-LA is an antioxidant with various benefits in treating diabetes, including managing symptomatic diabetic neuropathy. This study will test a novel and innovative strategy to synthesize a new isomer of lipoic acid (R-LA) derivatives (bifunctional NO-donor/antioxidant) in one chemical on homomeric and heteromeric AMPA receptor subunits. We used patch-clamp electrophysiology to examine LA derivatives expressed in human embryonic kidney 293 cells (HEK293) for inhibition and changes in desensitization or deactivation rates. LA derivatives were shown to be potent antagonists of AMPA receptors, with an 8-11-fold reduction in AMPA receptor currents seen following the delivery of the compounds. Furthermore, the LA derivatives influenced the rates of desensitization and deactivation of AMPA receptors. Based on our results, especially given that α-LA is closely connected to the nervous system, we may better understand using AMPA receptors and innovative drugs to treat neurological diseases associated with excessive activation of AMPA receptors.
Keywords: AMPA receptor; desensitization; inhibition; neuroprotective; α-Lipoic acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Affecting AMPA Receptor Biophysical Gating Properties with Negative Allosteric Modulators.Mol Neurobiol. 2022 Sep;59(9):5264-5275. doi: 10.1007/s12035-022-02913-4. Epub 2022 Jun 10. Mol Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 35687302 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the kinetics mechanism of AMPA receptor inhibition by 2-oxo-3H-benzoxazole derivatives.Bioorg Chem. 2022 Dec;129:106163. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2022.106163. Epub 2022 Sep 17. Bioorg Chem. 2022. PMID: 36137313
-
Inhibition and assessment of the biophysical gating properties of GluA2 and GluA2/A3 AMPA receptors using curcumin derivatives.PLoS One. 2019 Aug 27;14(8):e0221132. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0221132. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31454362 Free PMC article.
-
Diversity of AMPA Receptor Ligands: Chemotypes, Binding Modes, Mechanisms of Action, and Therapeutic Effects.Biomolecules. 2022 Dec 27;13(1):56. doi: 10.3390/biom13010056. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36671441 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacology of AMPA/kainate receptor ligands and their therapeutic potential in neurological and psychiatric disorders.Drugs. 2000 Jan;59(1):33-78. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200059010-00004. Drugs. 2000. PMID: 10718099 Review.
Cited by
-
Thiazole Derivatives as Modulators of GluA2 AMPA Receptors: Potent Allosteric Effects and Neuroprotective Potential.Biomolecules. 2023 Nov 23;13(12):1694. doi: 10.3390/biom13121694. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 38136566 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

