Lectin Analysis of SARS-CoV-2-Positive Nasopharyngeal Samples Using GLYcoPROFILE® Technology Platform
- PMID: 36428920
- PMCID: PMC9689752
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics12112860
Lectin Analysis of SARS-CoV-2-Positive Nasopharyngeal Samples Using GLYcoPROFILE® Technology Platform
Abstract
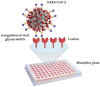
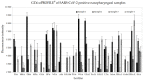
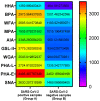
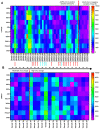
Nasopharyngeal samples are currently accepted as the standard diagnostic samples for nucleic acid amplification testing and antigenic testing for the SARS-CoV-2 virus. In addition to the diagnostic capacity of SARS-CoV-2-positive crude nasopharyngeal samples, their qualitative potential for direct glycan-specific analysis, in order to uncover unique glycol profiles, was assessed. In this study we provide glycan characterization of SARS-CoV-2-positive and -negative nasopharyngeal samples directly from lectin interactions. Although with limited throughput, this study evaluated the clinical sensitivity and specificity of the GLYcoPROFILE® technology platformon45crude nasopharyngeal samples collected between November 2020 and April 2022. Each GLYcoPROFILE® of 39 SARS-CoV-2-positive samples was compared toglycoprofiling on a panel of 10 selected lectins and the results were paralleled with SARS-CoV-2-negative samples’ results. The GLYcoPROFILE® showed a clear distinction between positive and negative samples with WFA, GSL-II, PHA-L (GlcNAc-specific) and BPA (GalNAc-specific) highlighted as relevant lectins in SARS-CoV-2-positive samples. In addition, a significant, positive statistical correlation was found for these lectins (p < 0.01).
Keywords: COVID-19; GLYcoPROFILE® technology; SARS-CoV-2; lectins; nasopharyngeal samples.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
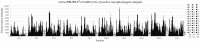
Similar articles
-
Clinical evaluation of the rapid nucleic acid amplification point-of-care test (Smart Gene SARS-CoV-2) in the analysis of nasopharyngeal and anterior nasal samples.J Infect Chemother. 2022 Apr;28(4):543-547. doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2021.12.027. Epub 2021 Dec 31. J Infect Chemother. 2022. PMID: 35016829 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of four different strategies for SARS-CoV-2 surveillance in the general population (CoV-Surv Study): a structured summary of a study protocol for a cluster-randomised, two-factorial controlled trial.Trials. 2021 Jan 8;22(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04982-z. Trials. 2021. PMID: 33419461 Free PMC article.
-
Randomized clinical trial to compare the efficacy of ivermectin versus placebo to negativize nasopharyngeal PCR in patients with early COVID-19 in Peru (SAINT-Peru): a structured summary of a study protocol for randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2021 Apr 9;22(1):262. doi: 10.1186/s13063-021-05236-2. Trials. 2021. PMID: 33836826 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 Evolutionary Adaptation toward Host Entry and Recognition of Receptor O-Acetyl Sialylation in Virus-Host Interaction.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 26;21(12):4549. doi: 10.3390/ijms21124549. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32604730 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Legume Lectins with Different Specificities as Potential Glycan Probes for Pathogenic Enveloped Viruses.Cells. 2022 Jan 20;11(3):339. doi: 10.3390/cells11030339. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35159151 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

