Regulation of Polyhomeotic Condensates by Intrinsically Disordered Sequences That Affect Chromatin Binding
- PMID: 36412795
- PMCID: PMC9680516
- DOI: 10.3390/epigenomes6040040
Regulation of Polyhomeotic Condensates by Intrinsically Disordered Sequences That Affect Chromatin Binding
Abstract
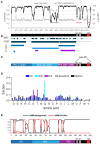
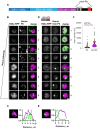
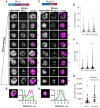
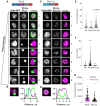
The Polycomb group (PcG) complex PRC1 localizes in the nucleus in condensed structures called Polycomb bodies. The PRC1 subunit Polyhomeotic (Ph) contains an oligomerizing sterile alpha motif (SAM) that is implicated in both PcG body formation and chromatin organization in Drosophila and mammalian cells. A truncated version of Ph containing the SAM (mini-Ph) forms phase-separated condensates with DNA or chromatin in vitro, suggesting that PcG bodies may form through SAM-driven phase separation. In cells, Ph forms multiple small condensates, while mini-Ph typically forms a single large nuclear condensate. We therefore hypothesized that sequences outside of mini-Ph, which are predicted to be intrinsically disordered, are required for proper condensate formation. We identified three distinct low-complexity regions in Ph based on sequence composition. We systematically tested the role of each of these sequences in Ph condensates using live imaging of transfected Drosophila S2 cells. Each sequence uniquely affected Ph SAM-dependent condensate size, number, and morphology, but the most dramatic effects occurred when the central, glutamine-rich intrinsically disordered region (IDR) was removed, which resulted in large Ph condensates. Like mini-Ph condensates, condensates lacking the glutamine-rich IDR excluded chromatin. Chromatin fractionation experiments indicated that the removal of the glutamine-rich IDR reduced chromatin binding and that the removal of either of the other IDRs increased chromatin binding. Our data suggest that all three IDRs, and functional interactions among them, regulate Ph condensate size and number. Our results can be explained by a model in which tight chromatin binding by Ph IDRs antagonizes Ph SAM-driven phase separation. Our observations highlight the complexity of regulation of biological condensates housed in single proteins.
Keywords: Drosophila; Polycomb; chromatin; condensate; intrinsically disordered region; phase separation; sterile alpha motif.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Two-Step Mechanism for Creating Stable, Condensed Chromatin with the Polycomb Complex PRC1.Molecules. 2024 Jan 9;29(2):323. doi: 10.3390/molecules29020323. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38257239 Free PMC article.
-
How a disordered linker in the Polycomb protein Polyhomeotic tunes phase separation and oligomerization.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Oct 27:2023.10.26.564264. doi: 10.1101/2023.10.26.564264. bioRxiv. 2023. PMID: 37961422 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Nuclear condensates of the Polycomb protein chromobox 2 (CBX2) assemble through phase separation.J Biol Chem. 2019 Feb 1;294(5):1451-1463. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.006620. Epub 2018 Dec 4. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30514760 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction modules that impart specificity to disordered protein.Trends Biochem Sci. 2023 May;48(5):477-490. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2023.01.004. Epub 2023 Feb 6. Trends Biochem Sci. 2023. PMID: 36754681 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Through the lens of phase separation: intrinsically unstructured protein and chromatin looping.Nucleus. 2023 Dec;14(1):2179766. doi: 10.1080/19491034.2023.2179766. Nucleus. 2023. PMID: 36821650 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Modularity of PRC1 composition and chromatin interaction define condensate properties.Mol Cell. 2024 May 2;84(9):1651-1666.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2024.03.001. Epub 2024 Mar 22. Mol Cell. 2024. PMID: 38521066
-
CBX7C⋅PHC2 interaction facilitates PRC1 assembly and modulates its phase separation properties.iScience. 2024 Mar 21;27(4):109548. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109548. eCollection 2024 Apr 19. iScience. 2024. PMID: 38600974 Free PMC article.
-
Dan forms condensates in neuroblasts and regulates nuclear architecture and progenitor competence in vivo.Nat Commun. 2024 Jun 14;15(1):5097. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-49326-6. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38877037 Free PMC article.
-
A Two-Step Mechanism for Creating Stable, Condensed Chromatin with the Polycomb Complex PRC1.Molecules. 2024 Jan 9;29(2):323. doi: 10.3390/molecules29020323. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38257239 Free PMC article.
-
How a disordered linker in the Polycomb protein Polyhomeotic tunes phase separation and oligomerization.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Oct 27:2023.10.26.564264. doi: 10.1101/2023.10.26.564264. bioRxiv. 2023. PMID: 37961422 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

