SIRT1 activation and its effect on intercalated disc proteins as a way to reduce doxorubicin cardiotoxicity
- PMID: 36408244
- PMCID: PMC9672938
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1035387
SIRT1 activation and its effect on intercalated disc proteins as a way to reduce doxorubicin cardiotoxicity
Erratum in
-
Erratum: SIRT1 activation and its effect on intercalated disc proteins as a way to reduce doxorubicin cardiotoxicity.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Feb 9;14:1154384. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1154384. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36843934 Free PMC article.
Abstract
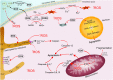
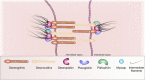
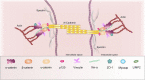
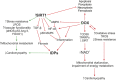
According to the World Health Organization, the neoplasm is one of the main reasons for morbidity and mortality worldwide. At the same time, application of cytostatic drugs like an independent type of cancer treatment and in combination with surgical methods, is often associated with the development of cardiovascular complications both in the early and in the delayed period of treatment. Doxorubicin (DOX) is the most commonly used cytotoxic anthracycline antibiotic. DOX can cause both acute and delayed side effects. The problem is still not solved, as evidenced by the continued activity of researchers in terms of developing approaches for the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular complications. It is known, the heart muscle consists of cardiomyocytes connected by intercalated discs (ID), which ensure the structural, electrical, metabolic unity of the heart. Various defects in the ID proteins can lead to the development of cardiovascular diseases of various etiologies, including DOX-induced cardiomyopathy. The search for ways to influence the functioning of ID proteins of the cardiac muscle can become the basis for the creation of new therapeutic approaches to the treatment and prevention of cardiac pathologies. SIRT1 may be an interesting cardioprotective variant due to its wide functional significance. SIRT1 activation triggers nuclear transcription programs that increase the efficiency of cellular, mitochondrial metabolism, increases resistance to oxidative stress, and promotes cell survival. It can be assumed that SIRT1 can not only provide a protective effect at the cardiomyocytes level, leading to an improvement in mitochondrial and metabolic functions, reducing the effects of oxidative stress and inflammatory processes, but also have a protective effect on the functioning of IDs structures of the cardiac muscle.
Keywords: NAD+; adherens junctions; desmosomes; doxorubicin cardiomyopathy; gap junction; heart failure; intercalated discs; sirtuins.
Copyright © 2022 Podyacheva and Toropova.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Erratum: SIRT1 activation and its effect on intercalated disc proteins as a way to reduce doxorubicin cardiotoxicity.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Feb 9;14:1154384. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1154384. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36843934 Free PMC article.
-
Unravelling the ultrastructural details of αT-catenin-deficient cell-cell contacts between heart muscle cells by the use of FIB-SEM.J Microsc. 2020 Sep;279(3):189-196. doi: 10.1111/jmi.12855. Epub 2019 Dec 22. J Microsc. 2020. PMID: 31828778
-
Doxorubicin induced cardio toxicity through sirtuins mediated mitochondrial disruption.Chem Biol Interact. 2022 Sep 25;365:110028. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2022.110028. Epub 2022 Jul 31. Chem Biol Interact. 2022. PMID: 35921947 Review.
-
The organization of adherens junctions and desmosomes at the cardiac intercalated disc is independent of gap junctions.J Cell Sci. 2003 Mar 1;116(Pt 5):875-85. doi: 10.1242/jcs.00258. J Cell Sci. 2003. PMID: 12571285
-
Doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity: from bioenergetic failure and cell death to cardiomyopathy.Med Res Rev. 2014 Jan;34(1):106-35. doi: 10.1002/med.21280. Epub 2013 Mar 11. Med Res Rev. 2014. PMID: 23494977 Review.
Cited by
-
Nrf2: a dark horse in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity.Cell Death Discov. 2023 Jul 26;9(1):261. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01565-0. Cell Death Discov. 2023. PMID: 37495572 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Growth hormone releasing peptide-6 (GHRP-6) prevents doxorubicin-induced myocardial and extra-myocardial damages by activating prosurvival mechanisms.Front Pharmacol. 2024 May 30;15:1402138. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1402138. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38873418 Free PMC article.
-
The mechanism and therapeutic strategies in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity: Role of programmed cell death.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2024 Oct;29(5):666-680. doi: 10.1016/j.cstres.2024.09.001. Epub 2024 Sep 27. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2024. PMID: 39343295 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ando K., Uemura K., Kuzuya A., Maesako M., Asada-Utsugi M., Kubota M., et al. (2011). N-cadherin regulates p38 MAPK signaling via association with JNK-associated leucine zipper protein: Implications for neurodegeneration in Alzheimer disease. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 7619–7628. 10.1074/jbc.M110.158477 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

