Increased AR expression in castration-resistant prostate cancer rapidly induces AR signaling reprogramming with the collaboration of EZH2
- PMID: 36408179
- PMCID: PMC9669968
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1021845
Increased AR expression in castration-resistant prostate cancer rapidly induces AR signaling reprogramming with the collaboration of EZH2
Abstract
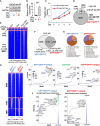
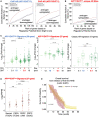
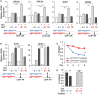
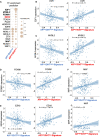
Elevated androgen receptor (AR) expression is a hallmark of castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) and contributes to the restoration of AR signaling under the conditions of androgen deprivation. However, whether overexpressed AR alone with the stimulation of castrate levels of androgens can be sufficient to induce the reprogramming of AR signaling for the adaptation of prostate cancer (PCa) cells remains unclear. In this study, we used a PCa model with inducible overexpression of AR to examine the acute effects of AR overexpression on its cistrome and transcriptome. Our results show that overexpression of AR alone in conjunction with lower androgen levels can rapidly redistribute AR chromatin binding and activates a distinct transcription program that is enriched for DNA damage repair pathways. Moreover, using a recently developed bioinformatic tool, we predicted the involvement of EZH2 in this AR reprogramming and subsequently identified a subset of AR/EZH2 co-targeting genes, which are overexpressed in CRPC and associated with worse patient outcomes. Mechanistically, we found that AR-EZH2 interaction is impaired by the pre-castration level of androgens but can be recovered by the post-castration level of androgens. Overall, our study provides new molecular insights into AR signaling reprogramming with the engagement of specific epigenetic factors.
Keywords: AR; CRPC; DNA damage repair; EZH2; androgen; androgen receptor; androgen-deprivation therapy; prostate cancer.
Copyright © 2022 Labaf, Li, Ting, Karno, Zhang, Gao, Patalano, Macoska, Zarringhalam, Han and Cai.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Epigenetic Reprogramming with Antisense Oligonucleotides Enhances the Effectiveness of Androgen Receptor Inhibition in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer.Cancer Res. 2018 Oct 15;78(20):5731-5740. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-0941. Epub 2018 Aug 22. Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30135193 Free PMC article.
-
Androgen receptors in hormone-dependent and castration-resistant prostate cancer.Pharmacol Ther. 2013 Dec;140(3):223-38. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.07.003. Epub 2013 Jul 13. Pharmacol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23859952 Review.
-
Restoration of the cellular secretory milieu overrides androgen dependence of in vivo generated castration resistant prostate cancer cells overexpressing the androgen receptor.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016 Jul 22;476(2):69-74. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.05.058. Epub 2016 May 12. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016. PMID: 27179779
-
Novel approach to therapeutic targeting of castration-resistant prostate cancer.Med Hypotheses. 2020 Feb 19;140:109639. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2020.109639. Online ahead of print. Med Hypotheses. 2020. PMID: 32097843
-
Androgen receptor: what we know and what we expect in castration-resistant prostate cancer.Int Urol Nephrol. 2018 Oct;50(10):1753-1764. doi: 10.1007/s11255-018-1964-0. Epub 2018 Aug 20. Int Urol Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 30128923 Review.
Cited by
-
Addressing the Reciprocal Crosstalk between the AR and the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathways for Prostate Cancer Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 24;24(3):2289. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032289. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768610 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sequence of androgen receptor-targeted vaccination with androgen deprivation therapy affects anti-prostate tumor efficacy.J Immunother Cancer. 2024 May 20;12(5):e008848. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2024-008848. J Immunother Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38772685 Free PMC article.
-
CDC20 Is Regulated by the Histone Methyltransferase, KMT5A, in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jul 13;15(14):3597. doi: 10.3390/cancers15143597. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37509260 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic Strategies for Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: Targeting AR-V7, Exploring Natural Compounds, and Optimizing FDA-Approved Therapies.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Aug 6;16(16):2777. doi: 10.3390/cancers16162777. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39199550 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of FKBP52 on cell proliferation and hormone-dependent cancers.Cancer Sci. 2023 Jul;114(7):2729-2738. doi: 10.1111/cas.15811. Epub 2023 Apr 27. Cancer Sci. 2023. PMID: 37026526 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

