Effect of citronellol on oxidative stress, neuroinflammation and autophagy pathways in an in vivo model of Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 36387498
- PMCID: PMC9663872
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e11434
Effect of citronellol on oxidative stress, neuroinflammation and autophagy pathways in an in vivo model of Parkinson's disease
Abstract
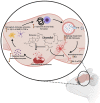
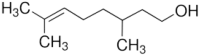
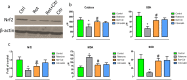
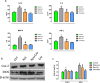
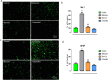
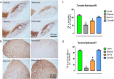
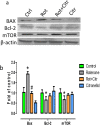
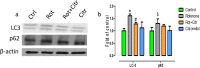
Citronellol, a monoterpene found in the essential oils of Cymbopogo plants has been reported to possess various biological properties. In the present study, we investigated the neuroprotective mechanisms of citronellol against rotenone induced neurodegeneration by using rat model of Parkinson's disease (PD). Our results demonstrated that oral administration of citronellol prevented rotenone induced reactive oxygen species production, lipid peroxidation and enhanced Nrf2 expression, catalase, glutathione peroxidase and superoxide dismutase levels in the brain. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays showed that citronellol reduced secretion of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 and decreased MMP-9 expression levels. Further, citronellol prevented rotenone induced microglia (Iba-1 staining) and astrocyte (GFAP staining) activation. Western blot analysis showed that citronellol significantly decreased the expression of cyclooxygenase-2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase-2 that are key markers of neuroinflammation. We further evaluated the effect of citronellol on dopaminergic neurons in substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc) and striatum (ST) which are key anatomical structures in PD. Tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) immunoreactivity showed that citronellol preserved Tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) positive dopaminergic neurons and enhanced TH striatal expression levels significantly compared to rotenone alone group. Further, to understand the effect of citronellol on apoptosis and proteotoxicity, we evaluated apoptotic markers (Bax, Bcl-2), growth regulator (mTOR) and α-synuclein expression. Citronellol attenuated rotenone induced expression of pro-apoptotic protein Bax, reduced α-synuclein expression and enhanced Bcl-2 and mTOR levels. In addition, citronellol modulated autophagy pathway by decreasing LC-3 (Microtubule-associated proteins) and p62 levels. Taken together, our results demonstrate that citronellol protected dopaminergic neurons through its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-apoptotic and autophagy modulating properties.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Citronellol; Dopaminergic neurons; Neuroprotection; Rotenone.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Myrcene Salvages Rotenone-Induced Loss of Dopaminergic Neurons by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, Apoptosis, and Autophagy.Molecules. 2023 Jan 10;28(2):685. doi: 10.3390/molecules28020685. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36677744 Free PMC article.
-
Glycyrrhizic acid Attenuates Neuroinflammation and Oxidative Stress in Rotenone Model of Parkinson's Disease.Neurotox Res. 2016 Feb;29(2):275-87. doi: 10.1007/s12640-015-9579-z. Epub 2015 Nov 25. Neurotox Res. 2016. PMID: 26607911
-
Lycopodium Attenuates Loss of Dopaminergic Neurons by Suppressing Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation in a Rat Model of Parkinson's Disease.Molecules. 2019 Jun 10;24(11):2182. doi: 10.3390/molecules24112182. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31185705 Free PMC article.
-
Protective role of apigenin on rotenone induced rat model of Parkinson's disease: Suppression of neuroinflammation and oxidative stress mediated apoptosis.Chem Biol Interact. 2017 May 1;269:67-79. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2017.03.016. Epub 2017 Apr 4. Chem Biol Interact. 2017. PMID: 28389404
-
Therapeutic potentials of plant iridoids in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases: A review.Eur J Med Chem. 2019 May 1;169:185-199. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.03.009. Epub 2019 Mar 8. Eur J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30877973 Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic Potential of Myrtenal and Its Derivatives-A Review.Life (Basel). 2023 Oct 20;13(10):2086. doi: 10.3390/life13102086. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37895468 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Targeting of Krüppel-Like Factor 4 and Its Pharmacological Potential in Parkinson's Disease: a Comprehensive Review.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Jun;61(6):3596-3606. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03800-2. Epub 2023 Nov 24. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 37996730 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammasomes Are Influenced by Epigenetic and Autophagy Mechanisms in Colorectal Cancer Signaling.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 3;25(11):6167. doi: 10.3390/ijms25116167. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38892354 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Essential Oil Molecules Can Break the Loop of Oxidative Stress in Neurodegenerative Diseases.Biology (Basel). 2023 Dec 7;12(12):1504. doi: 10.3390/biology12121504. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38132330 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Libertellenone C attenuates oxidative stress and neuroinflammation with the capacity of NLRP3 inhibition.Nat Prod Bioprospect. 2024 Feb 26;14(1):17. doi: 10.1007/s13659-024-00438-y. Nat Prod Bioprospect. 2024. PMID: 38407685 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zesiewicz T.A. Parkinson disease. Continuum. 2019;25(4):896–918. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

