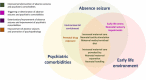
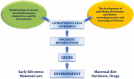
The impact of early-life environment on absence epilepsy and neuropsychiatric comorbidities
- PMID: 36386598
- PMCID: PMC9649966
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ibneur.2022.10.012
The impact of early-life environment on absence epilepsy and neuropsychiatric comorbidities
Abstract
This review discusses the long-term effects of early-life environment on epileptogenesis, epilepsy, and neuropsychiatric comorbidities with an emphasis on the absence epilepsy. The WAG/Rij rat strain is a well-validated genetic model of absence epilepsy with mild depression-like (dysthymia) comorbidity. Although pathologic phenotype in WAG/Rij rats is genetically determined, convincing evidence presented in this review suggests that the absence epilepsy and depression-like comorbidity in WAG/Rij rats may be governed by early-life events, such as prenatal drug exposure, early-life stress, neonatal maternal separation, neonatal handling, maternal care, environmental enrichment, neonatal sensory impairments, neonatal tactile stimulation, and maternal diet. The data, as presented here, indicate that some early environmental events can promote and accelerate the development of absence seizures and their neuropsychiatric comorbidities, while others may exert anti-epileptogenic and disease-modifying effects. The early environment can lead to phenotypic alterations in offspring due to epigenetic modifications of gene expression, which may have maladaptive consequences or represent a therapeutic value. Targeting DNA methylation with a maternal methyl-enriched diet during the perinatal period appears to be a new preventive epigenetic anti-absence therapy. A number of caveats related to the maternal methyl-enriched diet and prospects for future research are discussed.
Keywords: Absence epilepsy; Animal epilepsy model; Early environment; Epigenetic modification; Neuropsychiatric comorbidity; WAG/Rij.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Maternal Methyl-Enriched Diet Increases DNMT1, HCN1, and TH Gene Expression and Suppresses Absence Seizures and Comorbid Depression in Offspring of WAG/Rij Rats.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Jan 21;13(3):398. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13030398. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36766503 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal care exerts disease-modifying effects on genetic absence epilepsy and comorbid depression.Genes Brain Behav. 2018 Sep;17(7):e12477. doi: 10.1111/gbb.12477. Epub 2018 Apr 30. Genes Brain Behav. 2018. PMID: 29604188
-
The WAG/Rij strain: a genetic animal model of absence epilepsy with comorbidity of depression [corrected].Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2011 Jun 1;35(4):854-76. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2010.11.010. Epub 2010 Nov 17. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2011. PMID: 21093520 Review.
-
Gender-Dependent Effect of Maternal Methyl-Enriched Diet on the Expression of Genetic Absence Epilepsy and Comorbid Depression in Adult Offspring of WAG/Rij Rats.Dokl Biol Sci. 2020 Sep;494(1):244-247. doi: 10.1134/S0012496620050075. Epub 2020 Oct 20. Dokl Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33083882
-
Pharmacology of epileptogenesis and related comorbidities in the WAG/Rij rat model of genetic absence epilepsy.J Neurosci Methods. 2018 Dec 1;310:54-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2018.05.020. Epub 2018 May 29. J Neurosci Methods. 2018. PMID: 29857008 Review.
Cited by
-
The Effect of Maternal Exposure to Air Pollutants and Heavy Metals during Pregnancy on the Risk of Neurological Disorders Using the National Health Insurance Claims Data of South Korea.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 May 15;59(5):951. doi: 10.3390/medicina59050951. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 37241184 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal Methyl-Enriched Diet Increases DNMT1, HCN1, and TH Gene Expression and Suppresses Absence Seizures and Comorbid Depression in Offspring of WAG/Rij Rats.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Jan 21;13(3):398. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13030398. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36766503 Free PMC article.
-
The neuronal density in the rostral pole of substantia nigra pars compacta in Wistar Albino rats from Rijswijk rats: A link to spike-wave seizures.J Biol Methods. 2024 Sep 10;11(3):e99010022. doi: 10.14440/jbm.2024.0027. eCollection 2024. J Biol Methods. 2024. PMID: 39544190 Free PMC article.
-
Animal Models of Hypertension (ISIAH Rats), Catatonia (GC Rats), and Audiogenic Epilepsy (PM Rats) Developed by Breeding.Biomedicines. 2023 Jun 24;11(7):1814. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11071814. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37509453 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antidepressant and Anxiolytic Effects of L-Methionine in the WAG/Rij Rat Model of Depression Comorbid with Absence Epilepsy.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 4;24(15):12425. doi: 10.3390/ijms241512425. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569798 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
